Genome-Wide Genetic Architecture for Common Scab (Streptomyces scabei L.) Resistance in Diploid Potatoes
- PMID: 39940897
- PMCID: PMC11818057
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26031126
Genome-Wide Genetic Architecture for Common Scab (Streptomyces scabei L.) Resistance in Diploid Potatoes
Abstract
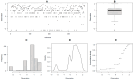
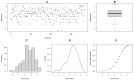
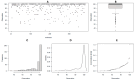
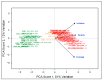
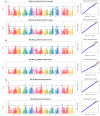
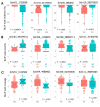
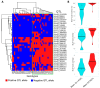
Most cultivated potato (Solanum tuberosum) varieties are highly susceptible to common scab (Streptomyces scabei). The disease is widespread in all major potato production areas and leads to high economic losses and food waste. Varietal resistance is seen as the most viable and sustainable long-term management strategy. However, resistant potato varieties are scarce, and their genetic architecture and resistance mechanisms are poorly understood. Moreover, diploid potato relatives to commercial potatoes remain to be fully explored. In the current study, a panel of 384 ethyl methane sulfonate (EMS)-mutagenized diploid potato clones were evaluated for common scab coverage, severity, and incidence traits under field conditions, and genome-wide association studies (GWASs) were conducted to dissect the genetic architecture of their traits. Using the GAPIT-MLM and RTM-GWAS statistical models, and Mann-Whitney non-parametric U-tests, we show that 58 QTNs/QTLs distributed on all 12 potato chromosomes were associated with common scab resistance, 52 of which had significant allelic effects on the three traits. In total, 38 of the 52 favorable QTNs/QTLs were found to be pleiotropic on at least two of the traits, while 14 were unique to a single trait and were found distributed over 3 chromosomes. The identified QTNs/QTLs showed low to high effects, highlighting the quantitative and multigenic inheritance of common scab resistance. The QTLs/QTNs associated with the three common scab traits were found to be co-located in genomic regions carrying 79 candidate genes playing roles in plant defense, cell wall component biosynthesis and modification, plant-pathogen interactions, and hormone signaling. A total of 61 potato clones were found to be tolerant or resistant to common scab. Taken together, the data show that the studied germplasm panel, the identified QTNs/QTLs, and the candidate genes are prime genetic resources for breeders and biologists in breeding and targeted gene editing.
Keywords: GWAS; Streptomyces scabei; candidate genes; common scab; diploid potato; disease resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genome-wide genetic architecture for plant maturity and drought tolerance in diploid potatoes.Front Genet. 2024 Jan 31;14:1306519. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1306519. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 38357658 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Trait Loci for Resistance to Common Scab and Cold-Induced Sweetening in Diploid Potato.Plant Genome. 2017 Nov;10(3). doi: 10.3835/plantgenome2016.10.0110. Plant Genome. 2017. PMID: 29293805
-
Genomic Selection for Late Blight and Common Scab Resistance in Tetraploid Potato (Solanum tuberosum).G3 (Bethesda). 2018 Jul 2;8(7):2471-2481. doi: 10.1534/g3.118.200273. G3 (Bethesda). 2018. PMID: 29794167 Free PMC article.
-
Bridging the gap between genome analysis and precision breeding in potato.Trends Genet. 2013 Apr;29(4):248-56. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2012.11.006. Epub 2012 Dec 20. Trends Genet. 2013. PMID: 23261028 Review.
-
Isolation and identification of an endophytic bacteria Bacillus sp. K-9 exhibiting biocontrol activity against potato common scab.Arch Microbiol. 2022 Jul 14;204(8):483. doi: 10.1007/s00203-022-02989-5. Arch Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35833995 Review.
References
-
- Leiminger J., Frank M., Wenk C., Poschenrieder G., Kellermann A., Schwarzfischer A. Distribution and characterization of Streptomyces species causing potato common scab in Germany. Plant Pathol. 2013;62:611–623. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3059.2012.02659.x. - DOI
-
- Braun S.R., Gevens A., Charkowski A., Allen C., Jansky S. Potato common scab: A review of the causal pathogens, management practices, varietal resistance screening methods, and host resistance. Am. J. Potato Res. 2017;94:283–296. doi: 10.1007/s12230-017-9575-3. - DOI
-
- Koizumi E., Igarashi T., Tsuyama M., Ogawa K., Asano K., Kobayashi A., Sanetomo R., Hosaka K. Association of genome-wide SNP markers with resistance to common scab of potato. Am. J. Potato Res. 2021;98:149–156. doi: 10.1007/s12230-021-09827-2. - DOI
-
- Al-Mughrabi K.I., Vikram A., Poirier R., Jayasuriya K., Moreau G. Management of common scab of potato in the field using biopesticides, fungicides, soil additives, or soil fumigants. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2015;25:125–135. doi: 10.1080/09583157.2015.1079809. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

