Progesterone Promotes Anti-Anxiety/Depressant-like Behavior and Trophic Actions of BDNF in the Hippocampus of Female Nuclear Progesterone Receptor, but Not 5α-Reductase, Knockout Mice
- PMID: 39940941
- PMCID: PMC11818940
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26031173
Progesterone Promotes Anti-Anxiety/Depressant-like Behavior and Trophic Actions of BDNF in the Hippocampus of Female Nuclear Progesterone Receptor, but Not 5α-Reductase, Knockout Mice
Abstract
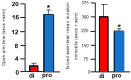
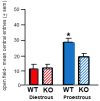
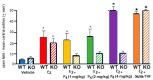
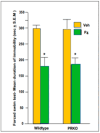
Progestogens' anti-anxiety and anti-depressive effects and mechanisms are not well-understood. Progestogens are hypothesized to have anti-anxiety and anti-depressive effects on behavior, independent of actions at nuclear progestin receptors (NPRs) and dependent on allopregnanolone (5α-pregnan-3α-ol-20-one; 3α,5α-THP), a 5α-reduced, neuroactive metabolite of progesterone (P4). Adult c57 mice in behavioral estrus (proestrus; pro) showed more anti-anxiety-like and anti-depressant-like behavior and higher levels of estradiol (E2), P4, and allopregnanolone in the hippocampus/amygdala complex. Proestrus c57 > 5α-reductase knockout (5αRKO) mice made more central entries in an open field than diestrus c57 and 5αRKO mice that were not different. Ovariectomized (OVX) c57 mice administered 1, 2, or 4 mg/kg P4 SC showed dosage-dependent increases in central entries in an open field (more anti-anxiety-like behavior); 5αRKO mice had maximal increases at 1-2 mg/kg P4. OVX c57 and 5αRKO mice showed maximum increases in central entries with SC 3α,5α-THP (4 mg/kg), and c57s showed a similar maximal response to P4 (4 mg/kg), but 5αRKOs response was half at that dosage. P4 (4 mg/kg SC to OVX c57 or progestin receptor knockout (PRKO) mice decreased immobility (depression-like behavior) in the forced swim task. Effects of E2 and veh were similar in both groups. Levels of 3α,5α-THP in the hippocampus/amygdala were consistent with effects on central entries in the open field. Levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the hippocampus/amygdala were greater among E2-primed (0.09 mg/kg, SC) vs vehicle-administered mice. In sum, adult female mice can be responsive to P4 for anti-anxiety/anti-depressant-like behavior; such effects may be independent of NPRs but require 5α-reduction and E2's priming actions at BDNF in the hippocampus/amygdala complex.
Keywords: elevated plus maze; forced swim; neuroactive steroid; neurosteroid; non-genomic; open field.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Patterson R., Balan I., Morrow A.L., Meltzer-Brody S. Novel neurosteroid therapeutics for post-partum depression: Perspectives on clinical trials, program development, active research, and future directions. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2024;49:67–72. doi: 10.1038/s41386-023-01721-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cable J.K., Grider M.H. StatPearls Internet. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2024. Physiology, Progesterone.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

