Evaluation of a Norcantharidin Nanoemulsion Efficacy for Treating B16F1-Induced Melanoma in a Syngeneic Murine Model
- PMID: 39940982
- PMCID: PMC11818190
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26031215
Evaluation of a Norcantharidin Nanoemulsion Efficacy for Treating B16F1-Induced Melanoma in a Syngeneic Murine Model
Abstract
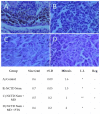
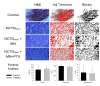
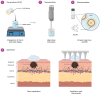
Melanoma, a lethal type of cancer originating from melanocytes, is the leading cause of death among skin cancers. While surgical excision of the lesions is the primary treatment for melanoma, not all cases are candidates for surgical procedures. New treatments and complementary options are necessary, given the increasing diagnosis rate. In the present study, a norcantharidin-containing nanoemulsion was developed and evaluated in vivo using a syngeneic graft murine model. Norcantharidin is the demethylated analog of cantharidin, known for its anticancer properties. Our model contemplates surgical excision surgery simulating the standard treatment and the role of the nanoemulsion as a potential adjuvant therapy. We observed a significant decrease in the growth rate of the melanoma lesion in the treated groups compared to the control group, both at the 20th and 30th days of treatment. Moreover, we evaluated the drug bioavailability in serum samples, and the results showed that norcantharidin was detectable in a range of 0.1 to 0.18 mg/mL in the treated groups. Furthermore, histopathological analysis was performed on the amputated tumors, where significant differences were found regarding size, mitosis rate, lymphocytic infiltration, and multispectral quantitative image analysis compared to the control group. If more clinical studies are conducted, the norcantharidin-containing nanoemulsion could be a potential alternative or adjuvant therapy. Topical nanosystems can become or complement standard therapies, which is needed as melanoma affects not only in terms of mortality but also the patient's morbidity and life quality.
Keywords: melanoma; nanoemulsion; nanosystems; nanotechnology; norcantharidin; topical administration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
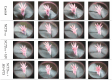
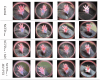
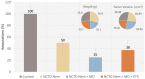
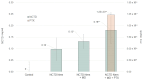
References
-
- IARC Publications. [(accessed on 28 June 2024)]. Available online: https://publications.iarc.fr/
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

