Histology of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract, Morphometry and Lymphocyte Subpopulations of the Duodenal Mucosa: Insights from Healthy Individuals
- PMID: 39941117
- PMCID: PMC11818500
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26031349
Histology of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract, Morphometry and Lymphocyte Subpopulations of the Duodenal Mucosa: Insights from Healthy Individuals
Abstract
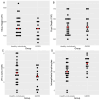
The upper oesophagogastrointestinal (UEGI) tract histology, intestinal morphometry and lymphocyte subpopulations of healthy people is scarcely known. In research studies of inflammation involving the UEGI tract, there is a lack of adequate healthy controls. Aims: To evaluate the histology of the UEGI tract and the duodenal lymphocyte subpopulations of healthy volunteers and patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), the latter to assess if it could replace healthy subjects. Healthy individuals were excluded if they had symptoms, comorbidities, pregnancy, toxics, medications or abnormal blood analysis. Subjects in both groups with abnormal duodenal intraepithelial lymphocyte (IEL) counts were also excluded. A total of 280 subjects were assessed, and 37 were included (23 healthy and 14 with GERD). The GERD group showed a higher IEL count (median [IQR]: 19.5 [17-22]), than healthy group: (15 [12-18]), p = 0.004. Eosinophils, mast cells and intestinal morphometry were similar in both groups. In the lamina propria, CD4+ T cells decreased (p = 0.008), and CD8+ T cells increased (p = 0.014). The total innate lymphoid cells (ILC) and CD3- cells decreased (p = 0.007) in GERD group compared to healthy controls. At the intraepithelial level, NKT cells increased (p = 0.036) and ILC3 decreased (p = 0.049) in the GERD group. This is the first study to comprehensively map the histology, morphometry and duodenal subpopulations of healthy volunteers to help define a "gold standard" of normality. The differences found between both groups suggest that, whenever possible, healthy subjects should be included in research studies. Alternatively, we can consider a well-defined homogenous group with GERD to serve as the control group.
Keywords: eosinophils; flow cytometry; healthy mucosa; innate lymphoid cells; intestinal morphometry; intraepithelial lymphocytes; mast cells; natural killer cells; γδ+ cells.
Conflict of interest statement
A. Martín-Cardona has received financial support for conference attendance, educational activities and research support from AbbVie, Biogen, Faes Farma, Ferring, Jannsen, MSD, Pfizer, Takeda, Dr. Falk Pharma, Lilly and Tillotts. R. Rifà has served as a speaker for Advanz and has received financial support for conference attendance and educational activities from Gilead, AbbVie, Roche, Advanz and Kern Pharma. Y. Zabana has received support for conference attendance, speaker fees, research support and consulting fees from: AbbVie, Adacyte, Alfa-Sigma, Almirall, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Dr Falk Pharma, FAES Pharma, Fresenius Kabi, Ferring, Galapagos, Janssen, J&J, Kern, Lilly, MSD, Otsuka, Pfizer, Sanofi, Shire, Takeda, Tillots. M. Esteve has received financial support for conference attendance and research support from Abbvie, Biogen, Faes Farma, Ferring, Jannsen, MSD, Pfizer, Takeda and Tillotts. F. Fernández-Bañares has received financial support for conference attendance and research support from AbbVie, Biogen, Faes Farma, Ferring, Jannsen, MSD, Pfizer, Takeda and Tillotts. The remaining authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Martín-Cardona A., Carrasco A., Arau B., Vidal J., Tristán E., Ferrer C., Gonzalez-Puglia G., Pallarès N., Tebé C., Farrais S., et al. Γδ+ T-Cells Is a Useful Biomarker for the Differential Diagnosis between Celiac Disease and Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity in Patients under Gluten Free Diet. Nutrients. 2024;16:2294. doi: 10.3390/nu16142294. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Esteve M., Salas A., Fernandez-Banares F., Lloreta J., Marine M., Gonzalez C.I., Forne M., Casalots J., Santaolalla R., Espinos J.C., et al. Intestinal Spirochetosis and Chronic Watery Diarrhea: Clinical and Histological Response to Treatment and Long-Term Follow Up. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006;21:1326–1333. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2006.04150.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pellegrino S., Villanacci V., Sansotta N., Scarfã R., Bassotti G., Vieni G., Princiotta A., Sferlazzas C., Magazzù G., Tuccari G. Redefining the Intraepithelial Lymphocytes Threshold to Diagnose Gluten Sensitivity in Patients with Architecturally Normal Duodenal Histology. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011;33:697–706. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2011.04578.x. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

