Large Italian Multicenter Study on Prognostic Value of Baselines Variables in mCRPC Patients Treated with 223RaCl2: Ten Years of Clinical Experience
- PMID: 39941269
- PMCID: PMC11817225
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15030339
Large Italian Multicenter Study on Prognostic Value of Baselines Variables in mCRPC Patients Treated with 223RaCl2: Ten Years of Clinical Experience
Abstract
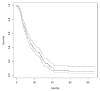
Background/Objectives: The prognostic value of baseline clinical parameters in predicting the survival prolonging effect of Radium-223-dichloride (223RaCl2) for metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) patients has been the object of intensive research and remains an open issue. This national multicenter study aimed to corroborate the evidence of ten years of clinical experience with 223RaCl2 by collecting data from eight Italian Nuclear Medicine Units. Methods: Data from 581 consecutive mCRPC patients treated with 223RaCl2 were retrospectively analyzed. Several baseline variables relevant to the overall survival (OS) analysis were considered, including age, previous radical prostatectomy/radiotherapy, number of previous treatment lines, prior chemotherapy, Gleason score, presence of lymphoadenopaties, number of bone metastases, concomitant use of bisphosphonates/Denosumab, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status (ECOG-PS), as well as baseline values of hemoglobin (Hb), platelets, Total Alkaline Phosphatase (tALP), Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH), and Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA). Data were summarized using descriptive statistics, univariate analysis and multivariate analysis with the Cox model. Results: The median OS time was 14 months (95%CI 12-17 months). At univariate analysis age, the number of previous treatment lines, number of bone metastases, ECOG-PS, presence of lymphadenopathies at the time of enrollment, as well as baseline tALP, PSA, and Hb, were independently associated with OS. After multivariate analysis, the number of previous treatment lines (HR = 1.1670, CI = 1.0095-1.3491, p = 0.0368), the prior chemotherapy (HR = 0.6461, CI = 0.4372-0.9549, p = 0.0284), the presence of lymphadenopathies (HR = 1.5083, CI = 1.1210-2.0296, p = 0.0066), the number of bone metastases (HR = 0.6990, CI = 0.5416-0.9020, p = 0.0059), ECOG-PS (HR = 1.3551, CI = 1.1238-1.6339, p = 0.0015), and baseline values of tALP (HR = 1.0008, CI = 1.0003-1.0013, p = 0.0016) and PSA (HR = 1.0004, CI = 1.0002-1.0006, p = 0.0005) remained statistically significant. Conclusions: In the era of precision medicine and in the landscape of novel therapies for mCRPC, the prognostic stratification of patients undergoing 223RaCl2 has a fundamental role for clinical decision-making, ranging from treatment choice to optimal sequencing and potential associations. This large Italian multicenter study corroborated the prognostic value of several variables, emerging from ten years of clinical experience with 223RaCl2.
Keywords: Radium-223; mCRPC; multicenter study; prostate cancer; radionuclide therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mohler J.L., Antonarakis E.S., Armstrong A.J., D’Amico A.V., Davis B.J., Dorff T., Eastham J.A., Enke C.A., Farrington T.A., Higano C.S., et al. Prostate Cancer, Version 2.2019, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2019;17:479–505. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2019.0023. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kassis A.I., Adelstein S.J. Radiobiologic Principles in Radionuclide Therapy. J. Nucl. Med. 2005;46((Suppl. S1)):4S–12S. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous