A Novel Method to Represent the Three-Dimensional Inclination of the Distal Radius Joint Surface
- PMID: 39941275
- PMCID: PMC11817736
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15030345
A Novel Method to Represent the Three-Dimensional Inclination of the Distal Radius Joint Surface
Abstract
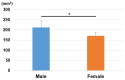
Objectives: This study aims to define three-dimensional (3D) parameters for the inclination of the distal radius joint surface. The goal is to develop standardized parameters for fracture reduction through comprehensive 3D evaluations of the joint surfaces. Methods: We analyzed 112 CT scans of unaffected wrists (56 males and 56 females) to construct 3D models of the distal radius. Using 3D coordinates, the normal vectors and angles were calculated based on three reference points on the distal radius joint surface. These normal vector components were then converted into unit vector components A, B, and C for the x, y, and z axes, respectively. Additionally, the angles of these unit vectors were assessed in the xy, yz, and xz planes. The 3D measurements were compared between males and females and against traditional two-dimensional (2D) parameters such as palmar tilt and radial inclination. Results: For males, the unit vector components were as follows: A: -0.14 ± 0.09, B: -0.92 ± 0.02, and C: -0.36 ± 0.07; for females, A: -0.21 ± 0.08, B: -0.90 ± 0.03, and C: -0.36 ± 0.05. Significant differences were found between males and females for the A and B vector components (representing the palmar-dorsal and proximal-distal axes, p < 0.01). The angles of the unit vectors in the xy, yz, and xz planes were 8.9 ± 5.4°/12.9 ± 5.0°, 21.3 ± 4.1°/22.1 ± 3.2°, and 22.2 ± 14.8°/28.8 ± 10.1° for males and females, respectively. There were significant differences between males and females in the angles of the xy and xz planes (sagittal and axial planes, p < 0.01). Strong correlations were observed between the xy-plane vectors and palmar tilt (r = 0.96), as well as between the yz-plane vectors and radial inclination (r = 0.88). Conclusions: This study evaluated the 3D inclination of the distal radius joint surface, revealing significant gender differences. This method, which also allows for the assessment of rotational alignment-difficult with conventional techniques-is expected to be a key 3D parameter in treating distal radius fractures.
Keywords: computed tomography; distal radius; joint inclination; rotational alignment; three-dimensional analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article.
Figures






References
-
- Petrie K.A., Burbank K., Sizer P.S., James C.R., Zumwalt M. Considerations of Sex Differences in Musculoskeletal Anatomy Between Males and Females. In: Robert-McComb J.J., Zumwalt M., Fernandez-del-Valle M., editors. The Active Female: Health Issues Throughout the Lifespan. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2023. pp. 3–24.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

