Alzheimer's Prediction Methods with Harris Hawks Optimization (HHO) and Deep Learning-Based Approach Using an MLP-LSTM Hybrid Network
- PMID: 39941306
- PMCID: PMC11816878
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15030377
Alzheimer's Prediction Methods with Harris Hawks Optimization (HHO) and Deep Learning-Based Approach Using an MLP-LSTM Hybrid Network
Abstract
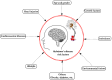
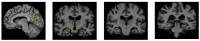
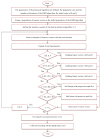
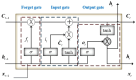
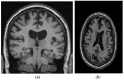
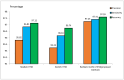
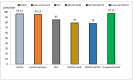
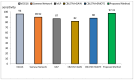
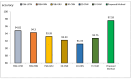
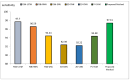
Background/Objective: Alzheimer's disease is a progressive brain syndrome causing cognitive decline and, ultimately, death. Early diagnosis is essential for timely medical intervention, with MRI medical imaging serving as a primary diagnostic tool. Machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) methods are increasingly utilized to analyze these images, but accurately distinguishing between healthy and diseased states remains a challenge. This study aims to address these limitations by developing an integrated approach combining swarm intelligence with ML and DL techniques for Alzheimer's disease classification. Method: This proposal methodology involves sourcing Alzheimer's disease-related MRI images and extracting features using convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and the Gray Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM). The Harris Hawks Optimization (HHO) algorithm is applied to select the most significant features. The selected features are used to train a multi-layer perceptron (MLP) neural network and further processed using a long short-term (LSTM) memory network in order to classify tumors as malignant or benign. The Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) dataset is utilized for assessment. Results: The proposed method achieved a classification accuracy of 97.59%, sensitivity of 97.41%, and precision of 97.25%, outperforming other models, including VGG16, GLCM, and ResNet-50, in diagnosing Alzheimer's disease. Conclusions: The results demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed approach in enhancing Alzheimer's disease diagnosis through improved feature extraction and selection techniques. These findings highlight the potential for advanced ML and DL integration to improve diagnostic tools in medical imaging applications.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Harris Hawks Optimization (HHO) algorithm; LSTM neural network; convolutional neural network (CNN); magnetic resonance images (MRI).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Alzheimer's Disease Prediction Using Fisher Mantis Optimization and Hybrid Deep Learning Models.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jun 6;15(12):1449. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15121449. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40564769 Free PMC article.
-
A hybrid multimodal machine learning model for Detecting Alzheimer's disease.Comput Biol Med. 2024 Mar;170:108035. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2024.108035. Epub 2024 Feb 3. Comput Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 38325214
-
Alzheimer's disease classification by supervised and intelligent techniques.J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2025 Jan 13;9:25424823241311838. doi: 10.1177/25424823241311838. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2025. PMID: 40034511 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning methods for predicting progression from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer's disease dementia: a systematic review.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2021 Sep 28;13(1):162. doi: 10.1186/s13195-021-00900-w. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34583745 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Review on Deep Learning Techniques in Alzheimer's Disease Diagnosis.Curr Top Med Chem. 2025;25(4):335-349. doi: 10.2174/0115680266310776240524061252. Curr Top Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 38847164 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advancements in Neuroimaging-Based Alzheimer's Disease Prediction Using Deep Learning Approaches in e-Health: A Systematic Review.Health Sci Rep. 2025 May 5;8(5):e70802. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.70802. eCollection 2025 May. Health Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40330773 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Habuza T., Zaki N., Mohamed E.A., Statsenko Y. Deviation from model of normal aging in alzheimer’s disease: Application of deep learning to structural MRI data and cognitive tests. IEEE Access. 2022;10:53234–53249. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3174601. - DOI
-
- Kabir M.T., Uddin M.S., Begum M., Thangapandiyan S., Rahman M.S., Aleya L., Mathew B., Ahmed M., Barreto G.E., Ashraf G.M. Cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease: Multitargeting strategy based on anti-Alzheimer’s drugs repositioning. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019;25:3519–3535. doi: 10.2174/1381612825666191008103141. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

