Cardiac Morpho-Functional Changes, Inflammation and Fibrosis in Systemic Sclerosis-A Pilot Study of a Tertiary Center Cohort
- PMID: 39941322
- PMCID: PMC11817609
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15030393
Cardiac Morpho-Functional Changes, Inflammation and Fibrosis in Systemic Sclerosis-A Pilot Study of a Tertiary Center Cohort
Abstract
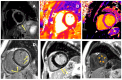
Background: Cardiac involvement (CI) in systemic sclerosis (SSc) is frequently subclinical and it can be identified in up to 80% of autopsied hearts. If present, symptoms are related to adverse prognosis, and CI represents one of the predominant causes of SSc-related mortality. Methods: A total of 20 patients with a diagnosis of SSc were included and followed up, and 37 volunteers were included and subsequently scanned on a 1.5T MR system. Results: Overall, thirteen (65%) patients had one or more abnormal cardiac findings in CMR (defined as CI[+]), of which in seven (35%), baseline ECGs and standard echocardiograms were normal or unspecific. Compared to healthy volunteers, SSc patients had a lower LVEF% (56.6% vs. 61.6%; p = 0.0131), longer T1 (1028.3 ms vs. 993.1 ms; p = 0.0049) and T2 relaxation times (48.24 ms vs. 43 ms p = 0.0011), and higher extracellular volume (ECV, 27.9% vs. 26.0%; p = 0.0112). However, no difference in CMR-derived, feature-tracking GLS values between patients and healthy controls was found (-15.5[2,8] vs. -16.3[1,1], respectively, p = 0.11). Over 3.4 (1.9-5.5) years, three patients (15%) died, and two others (10%) sustained major cardiac complications. Conclusions: Cardiac magnetic resonance with modern quantitative techniques reveals subtle morpho-functional alterations and thus allows for early diagnosis of myocardial involvement in systemic sclerosis. Our findings emphasize the need for extended diagnostic workup in these patients and demonstrate the ability of cardiac MR to select patients requiring closer follow-up and/or treatment decisions.
Keywords: cardiac magnetic resonance; heart involvement; systemic sclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Follansbee W.P., Marroquin O.C. Cardiac involvement in systemic sclerosis. In: Clemens P.J., Furst D.E., editors. Systemic Sclerosis. LWW; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2004. pp. 195–220.
-
- Bruni C., Buch M.H., Furst D.E., De Luca G., Djokovic A., Dumitru R.B., Giollo A., Polovina M., Steelandt A., Bratis K., et al. Primary systemic sclerosis heart involvement: A systematic literature review and preliminary data-driven, consensus-based WSF/HFA definition. J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2021;7:24–32. doi: 10.1177/23971983211053246. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

