Nanotechnology and Artificial Intelligence in Dyslipidemia Management-Cardiovascular Disease: Advances, Challenges, and Future Perspectives
- PMID: 39941558
- PMCID: PMC11818864
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14030887
Nanotechnology and Artificial Intelligence in Dyslipidemia Management-Cardiovascular Disease: Advances, Challenges, and Future Perspectives
Abstract
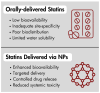
This narrative review explores emerging technologies in dyslipidemia management, focusing on nanotechnology and artificial intelligence (AI). It examines the current treatment recommendations and contrasts them with the future prospects enabled by these innovations. Nanotechnology shows significant potential in enhancing drug delivery systems, enabling more targeted and efficient lipid-lowering therapies. In parallel, AI offers advancements in diagnostics, cardiovascular risk prediction, and personalized treatment strategies. AI-based decision support systems and machine learning algorithms are particularly promising for analyzing large datasets and delivering evidence-based recommendations. Together, these technologies hold the potential to revolutionize dyslipidemia management, improving outcomes and optimizing patient care. In addition, this review covers key topics such as cardiovascular disease biomarkers and risk factors, providing insights into the current methods for assessing cardiovascular risk. It also discusses the current understanding of dyslipidemia, including pathophysiology and clinical management. Together, these insights and technologies hold the potential to revolutionize dyslipidemia management, improving outcomes and optimizing patient care.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; cardiovascular disease; cardiovascular risk-related biomarkers; dyslipidemia; emerging lipid-lowering therapies; nanotechnology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Global Cardiovascular Risk Consortium. Magnussen C., Ojeda F.M., Leong D.P., Alegre-Diaz J., Amouyel P., Aviles-Santa L., De Bacquer D., Ballantyne C.M., Bernabé-Ortiz A., et al. Global Effect of Modifiable Risk Factors on Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023;389:1273–1285. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2206916. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Medina-Leyte D.J., Zepeda-García O., Domínguez-Pérez M., González-Garrido A., Villarreal-Molina T., Jacobo-Albavera L. Endothelial Dysfunction, Inflammation and Coronary Artery Disease: Potential Biomarkers and Promising Therapeutical Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021;22:3850. doi: 10.3390/ijms22083850. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

