Role of Mirikizumab in the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease-From Bench to Bedside
- PMID: 39941671
- PMCID: PMC11818495
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14031001
Role of Mirikizumab in the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease-From Bench to Bedside
Abstract
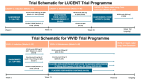
Mirikizumab is a monoclonal antibody directed against the p19 subunit of interleukin (IL)-23 to inhibit its interaction with the IL-23 receptor. IL-23 is a key cytokine involved in initiating and perpetuating the inflammatory cascade in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Mirikizumab is the first agent from the novel anti-IL-23p19 drug class to be licensed for ulcerative colitis and the first to present long-term endoscopic, histologic, symptomatic, and quality-of-life outcomes. More recently, the VIVID trial programme has led to the approval of mirikizumab in moderate to severe Crohn's disease. This review explores the history of its development, discusses key immunopharmacological properties unique to the drug, and details the available clinical trials and real-world evidence supporting its use in IBD.
Keywords: IL-23p19 inhibitor; inflammatory bowel disease; mirikizumab.
Conflict of interest statement
M.C. served as a speaker and an advisory board member of or has received grants from Pfizer, Celltrion, Ferring, and Dr. Falk. J.C. served as a speaker and an advisory board member of or has received grants from Abbvie, Takeda, Lilly, Johnson and Johnson, and Galapagos. J.C. is an associated editor of Frontline Gastroenterology. S.B. has had speaker arrangements with Takeda and Dr. Falk, has received a travel grant from Galapagos, and has provided consultancy to Galapagos. R.P. and A.P. have no conflicts of interest. K.P. has received honoraria for educational meetings and speaker fees from Abbvie, Janssen, Takeda, Dr. Falk Pharma, PredictImmune, Pfizer, and Ferring and has received advisory board fees from Abbvie, Galapagos, Pfizer, and Janssen. S.H. served as a speaker, a consultant, and an advisory board member or has received grants from Pfizer, Janssen, AbbVie, Takeda, Ferring, Lilly, Pharmacosmos, and Banook Group.
Figures

References
-
- Sanchez A.P., da Costa A., Del Rey C., Silva B., Romiti R. The Overview of the Immunobiology of Interleukin-23 Associated With Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Disorders: A Narrative Review. J. Drugs Dermatol. JDD. 2023;22:375–385. - PubMed
-
- Krueger J.G., Eyerich K., Kuchroo V.K., Ritchlin C.T., Abreu M.T., Elloso M.M., Fourie A., Fakharzadeh S., Sherlock J.P., Yang Y.W., et al. IL-23 past, present, and future: A roadmap to advancing IL-23 science and therapy. Front. Immunol. 2024;15:1331217. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1331217. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

