Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications of Long Non-coding RNAs in Cutaneous Biology and Disease
- PMID: 39943735
- PMCID: PMC11939017
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.70006
Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications of Long Non-coding RNAs in Cutaneous Biology and Disease
Abstract
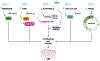
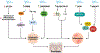
Human skin is the largest organ of the human body and accounts for approximately fifteen percent of the total bodyweight. Its main physiological role is to protect the body against a wide range of environmental factors including pathogens, ultraviolet light, and injury. Importantly, the skin can regenerate and heal upon injury in large part by the differentiation of keratinocytes. Not surprisingly, dysregulation of cutaneous differentiation and self-renewal can result in a variety of skin-related pathologies, including autoimmune disease and cancer. Increasing evidence supports the premise that long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) act as critical mediators of gene expression and regulate important biological processes within the skin. Notably, dysregulation of lncRNAs has been shown to influence diverse physiological and pathological consequences. More recently, numerous reports have revealed new mechanistic insight on the role that lncRNAs play in skin homeostasis as well as their contribution to the pathogenesis of skin-related disorders. Here, we review the biological functions of cutaneous lncRNAs and their impact on skin homeostasis. We also describe the fundamental roles of lncRNAs in the pathogenesis of skin-related disorders, including fibrotic, autoimmune, and malignant diseases. Lastly, we will highlight how a better understanding of lncRNAs at the molecular level may reveal novel therapeutic approaches for the improvement of cutaneous disorders.
Keywords: cancer; cutaneous biology; differentiation; lncRNA; pathology; skin.
© 2025 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest
Ozgur Sahin is the cofounder of Oncocube Therapeutics LLC, the founder and president of Loxigen Inc., and a member of the scientific advisory board for A2A Pharmaceuticals. All other authors have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long non-coding RNAs in cutaneous biology and proliferative skin diseases: Advances and perspectives.Cell Prolif. 2020 Jan;53(1):e12698. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12698. Epub 2019 Oct 6. Cell Prolif. 2020. PMID: 31588640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non-coding RNAs in cutaneous biology and keratinocyte carcinomas.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 Nov;77(22):4601-4614. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03554-3. Epub 2020 May 27. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32462404 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The non-coding skin: exploring the roles of long non-coding RNAs in epidermal homeostasis and disease.Bioessays. 2013 Dec;35(12):1093-100. doi: 10.1002/bies.201300068. Epub 2013 Sep 25. Bioessays. 2013. PMID: 24115003 Review.
-
Analysis of long non-coding RNAs highlights tissue-specific expression patterns and epigenetic profiles in normal and psoriatic skin.Genome Biol. 2015 Jan 30;16(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0570-4. Genome Biol. 2015. PMID: 25723451 Free PMC article.
-
RNA Sequencing Reveals the Long Non-Coding RNA Signature in Psoriasis Keratinocytes and Identifies CYDAER as a Long Non-Coding RNA Regulating Epidermal Differentiation.Exp Dermatol. 2025 Feb;34(2):e70054. doi: 10.1111/exd.70054. Exp Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 39953783 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Long Non-Coding TP73-AS1: A Potential Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 20;26(8):3886. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083886. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332793 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arda O, Göksügür N, and Tüzün Y. 2014. “Basic Histological Structure and Functions of Facial Skin.” Clinics in Dermatology 32, no. 1: 3–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R00 CA241367/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA193201/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM119512/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- A. Zuccotti and G.D.S. Ferretti were supported by the MUSC Hollings Cancer Center Postdoctoral Fellowship Program. F. Al-Fatyan was supported by NIH T32 CA193201. D.T. Long was supported by NIH R35 GM119512. O. Sahin was supported in part by NIH R01 CA251374 and NIH R01 CA267101. J. Rodriguez-Blanco was supported by NIH K01 NS119351, a Rally Foundation Career Development Award (20CDN46), a V Foundation Scholar Award (V2022-008), a Vince Lombardi Cancer Foundation Grant and an Alex's Lemonade Stand Foundation "A" award (23-28298). T. Barnoud was supported by NIH R00 CA241367. Additional funding was awarded in the form of a pilot project to T. Barnoud from the MUSC COBRE in Digestive and Liver Disease (NIH P20 GM130457).
- P20 GM130457/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

