Predictive value of miR-582-5p for onset of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury and its functional role during disease development
- PMID: 39944255
- PMCID: PMC11811718
- DOI: 10.5114/ceji.2024.145730
Predictive value of miR-582-5p for onset of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury and its functional role during disease development
Abstract
Introduction: Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common complication of sepsis, characterized by sharply declining renal function. As a global concern, understanding its pathogenesis and improving diagnosis and therapy face significant challenges. MicroRNAs are involved in the progression of a variety of diseases.This research was focused on differences in expression and clinical predictive value of miR-582-5p in sepsis-induced AKI.
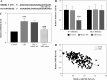
Material and methods: Blood and urine samples were collected from 180 patients. Sepsis-induced AKI was imitated in vitro by human kidney 2 (HK2) cells treated with 10 µg/ml lipopolysaccharide (LPS). The relative expression of miR-582-5p and HMGB2 in different conditions was quantified by qRT-PCR. Regulation of gene expression was performed by cell transfection. Cell viability and apoptosis were detected subsequently. Kidney injury and inflammatory assessment were analyzed by means of ELISA. Estimation of oxidative stress was performed using the corresponding kit. The dual luciferase reporter system verified the targeting relationship between miR-582-5p and HMGB2.
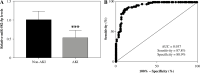
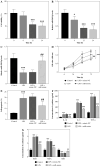
Results: Relative expression of miR-582-5p was lower in sepsis patients who suffered AKI later, along with LPS-induced HK2 cells. Both weak viability and elevated apoptosis were reversed by up-regulated miR-582-5p in HK2 cells exposed to LPS. In addition, the concentration of inflammatory factors and oxidation levels showed a significant decrease, based on up-regulated miR-582-5p. The clinical predictive value of miR-582-5p was visualized by a ROC curve with high sensitivity and specificity.
Conclusions: Up-regulated miR-582-5p reduced sepsis-induced AKI, and HMGB2 was a potential downstream target of miR-582-5p.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; miR-582-5p; sepsis.
Copyright © 2024 Termedia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes lipopolysaccharide-induced injury in human tubule epithelial cells by regulating miR-93-5p/TXNIP axis.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2021 Jun;210(2-3):121-132. doi: 10.1007/s00430-021-00705-6. Epub 2021 Apr 22. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33885954
-
Silencing circ_0074371 inhibits the progression of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by regulating miR-330-5p/ELK1 axis.Mamm Genome. 2022 Dec;33(4):642-653. doi: 10.1007/s00335-022-09961-0. Epub 2022 Aug 22. Mamm Genome. 2022. PMID: 35994105
-
MiR-150-5p protects against septic acute kidney injury via repressing the MEKK3/JNK pathway.Cell Signal. 2021 Oct;86:110101. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2021.110101. Epub 2021 Jul 30. Cell Signal. 2021. PMID: 34333083
-
Knockdown of circ-FANCA alleviates LPS-induced HK2 cell injury via targeting miR-93-5p/OXSR1 axis in septic acute kidney injury.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2021 Jan 19;13(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s13098-021-00625-8. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2021. PMID: 33468219 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA NKILA knockdown promotes cell viability and represses cell apoptosis, autophagy and inflammation in lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis model by regulating miR-140-5p/CLDN2 axis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021 Jun 25;559:8-14. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.04.074. Epub 2021 Apr 28. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021. PMID: 33932903
References
-
- Uchino S, Kellum JA, Bellomo R, et al. . (2005): Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: a multinational, multicenter study. JAMA 294: 813-818. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
