LncRNA RMRP promotes chondrocyte injury by regulating the FOXC1/RBP4 axis
- PMID: 39944260
- PMCID: PMC11811726
- DOI: 10.5114/ceji.2024.145312
LncRNA RMRP promotes chondrocyte injury by regulating the FOXC1/RBP4 axis
Abstract
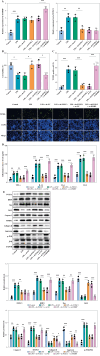
Introduction: The main pathological feature of osteoarthritis (OA) is chondrocyte injury. LncRNA mitochondrial RNA processing endoribonuclease (RMRP) has been shown to be a chondrogenic differentiation factor. This study aimed to explore the role of RMRP in chondrocyte injury.
Material and methods: Cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) and TUNEL assays were used to determine lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced chondrocyte viability and apoptosis, respectively. The interaction between RMRP and FOXC1 was analyzed by RIP and RNA pull-down. Dual luciferase reporter and ChIP were employed to analyze the interaction between FOXC1 and RBP4. The levels of RMRP, FOXC1, RBP4, apoptosis-related and extracellular matrix (ECM)-related genes were detected by RT-qPCR and western blot. ELISA assay was used for detection of inflammatory cytokines in LPS-induced chondrocytes.
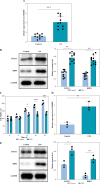
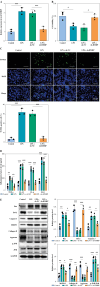
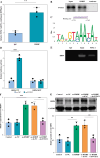
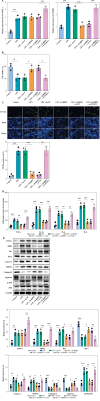
Results: The levels of RMRP, FOXC1 and RBP4 were significantly upregulated in OA cartilage tissues and LPS-induced chondrocytes. Knockdown of RMRP inhibited chondrocyte apoptosis and inflammation under LPS. RMRP interacted with FOXC1 and promoted RBP4 expression. FOXC1 could upregulate RBP4 and promote LPS-induced chondrocyte apoptosis and inflammation. Similarly, RMRP combined with FOXC1 and aggravated apoptosis and inflammation in LPS-treated chondrocytes.
Conclusions: RMRP promoted upregulation of RBP4 and activation of the JNK signaling pathway by binding to FOXC1, thereby accelerating LPS-induced apoptosis and inflammation in chondrocytes.
Keywords: FOXC1; RBP4; chondrocyte injury; lncRNA RMRP; osteoarthritis.
Copyright © 2024 Termedia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Y-box binding protein 1 stabilizes EP300 mRNA and promotes forkhead box C1 H3K27Ac to aggravate chondrocyte injury in osteoarthritis.J Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Jul 23;19(3):e70028. doi: 10.1002/ccs3.70028. eCollection 2025 Sep. J Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 40703976 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA RMRP knockdown promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in osteoarthritis chondrocytes by miR-206/CDK9 axis.Pharmazie. 2020 Oct 1;75(10):500-504. doi: 10.1691/ph.2020.0591. Pharmazie. 2020. PMID: 33305725
-
Differentiation Antagonizing Non-protein Coding RNA Knockdown Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Injury and Apoptosis in Human Chondrocyte Primary Chondrocyte Cells Through Upregulating miRNA-19a-3p.Orthop Surg. 2021 Feb;13(1):276-284. doi: 10.1111/os.12845. Epub 2020 Dec 6. Orthop Surg. 2021. PMID: 33283483 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA HOTAIR modulates chondrocyte apoptosis and inflammation in osteoarthritis via regulating miR-1277-5p/SGTB axis.Wound Repair Regen. 2021 May;29(3):495-504. doi: 10.1111/wrr.12908. Epub 2021 Mar 15. Wound Repair Regen. 2021. PMID: 33721916
-
Knockdown of lncRNA MFI2-AS1 inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced osteoarthritis progression by miR-130a-3p/TCF4.Life Sci. 2020 Jan 1;240:117019. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117019. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31678554 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA Polymerase III-Transcribed RNAs in Health and Disease: Mechanisms, Dysfunction, and Future Directions.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 18;26(12):5852. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125852. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40565315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Y-box binding protein 1 stabilizes EP300 mRNA and promotes forkhead box C1 H3K27Ac to aggravate chondrocyte injury in osteoarthritis.J Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Jul 23;19(3):e70028. doi: 10.1002/ccs3.70028. eCollection 2025 Sep. J Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 40703976 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
