Eco-friendly synthesis of NiO and Ag/NiO nanoparticles: applications in photocatalytic and antibacterial activities
- PMID: 39944296
- PMCID: PMC11813582
- DOI: 10.1098/rsos.241733
Eco-friendly synthesis of NiO and Ag/NiO nanoparticles: applications in photocatalytic and antibacterial activities
Abstract
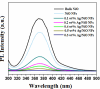
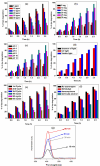
Herein, NiO and Ag/NiO NPs were produced via the solution combustion method using nickel nitrate and silver nitrate as oxidizers and Cocos nucifera water as a fuel at 450°C. The study also explores their applications in photocatalytic dye degradation, H2 production and antibacterial properties. The primary advantage of using C. nucifera water as a green fuel in the solution combustion method is that it serves a dual purpose-both as a fuel and as a solvent. This eliminates the need for additional water to create a homogeneous redox mixture of fuel and oxidant in the experimental procedure. X-ray diffraction confirmed the existence of Ag in the bunsenite form of rhombohedral structure with a simple cubic system, with particles sized at 31-44 nm. Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy revealed Ni, O and Ag weight percentages of 48.2, 44.5 and 7.3%, respectively. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy confirmed the formation of Ag in NiO nanostructure. UV-visible spectrometry showed reduced band gap energy of Ag/NiO NPs (3.03-2.87 eV) compared to the bare NiO NPs (3.21 eV), red shift of the optical response towards the visible region after doping Ag into the NiO. The 0.3 wt% Ag/NiO NPs showed the highest quantum efficiency (0.781) among the other synthesized NPs. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy revealed absorption bands in the range of 460-900 cm-1 stretching vibrations of Ni-O and Ag-O. Photoluminescence spectroscopy indicated that a doping concentration of 0.3 wt% Ag effectively introduces donor levels, defect levels and surface trap states within the NiO nanocrystalline structure, enhancing charge carrier separation and reducing recombination. Scanning electron microscopy revealed a voluminous, porous surface morphology characterized by numerous voids, resulting from the release of various combustible gases during the combustion process. Transmission electron microscopy images showed that most particles were spherical, irregular in size and well-distributed, with minimal aggregation with an average particle size of 25.8 nm. BET analysis of both NiO and 0.3 wt% Ag/NiO NPs exhibited type IV adsorption isotherms, indicating mesoporous structures and a clear monolayer-multilayer adsorption process, 0.3 wt% Ag/NiO NPs showed the highest surface area (170 m2 g-1) compared to the NiO (130 m2 g-1) NPs. Ag/NiO NPs has demonstrated a promising H2 evolution rate of 1212 μmol g⁻¹ under visible light illumination in a water/ethanol system. The trypan blue dye degradation reaches up to 98% and has moderate stability for the reusable photocatalysis process. The synthesized NPs exhibited significantly enhanced antibacterial activity against a range of bacterial strains.
Keywords: Ag/NiO NPs; Cocos nucifera; H2 production; NiO NPs; dye; photocatalysis.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no competing interests.
Figures








References
-
- Massoud-Sharifi A, Kara GK, Rabbani M. 2020. CuFe2O4@CuO: A Magnetic Composite Synthesized by Ultrasound Irradiation and Degradation of Methylene Blue on Its Surface in the Presence of Sunlight. Proceedings 48, 17. (10.3390/ECWS-4-06438)) - DOI
-
- He G, Wan M, Wang Z, Zhou X, Zhao Y, Sun L. 2023. A simple surface modification method to prepare versatile PVDF electrospun nanofibrous felts for separation, sterilization and degradation. Prog. Org. Coatings 182, 107664. (10.1016/j.porgcoat.2023.107664) - DOI
-
- Peter D, Jolla K, Bálint A, Thomas F, Ladislaw K. 2016. Water splitting and the band edge positions of TiO2,Electochimica Acta 199, 27–34. (10.1016/j.electacta.2016.03.122)) - DOI
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

