Functional and structural characterization of mouse Factor H-related B protein unveils a novel dimerization domain shared by FHR-B and FH
- PMID: 39944688
- PMCID: PMC11813886
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1522651
Functional and structural characterization of mouse Factor H-related B protein unveils a novel dimerization domain shared by FHR-B and FH
Abstract
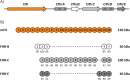
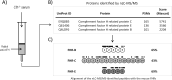
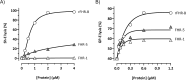
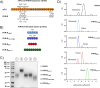
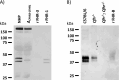
Factor H-related proteins (FHRs) are found in mice, but their equivalence to human FHRs remains uncertain. This study identifies three FHRs in mouse plasma (FHR-B, FHR-C, and FHR-E) and focuses on characterizing FHR-B. Using purified plasma proteins and recombinant mutants, FHR-B was found to form dimers and bind strongly to C3, C3b, iC3b, and C3dg. It also competes with mouse Factor H (mFH) for binding to C3b-coated surfaces and disrupts mFH regulation in hemolysis assays with sheep and guinea pig erythrocytes. These functions are localized to the C-terminal region and are dependent on FHR-B dimerization. Dimerization occurs through the N-terminal region (SCR1-3), which differs from mFH SCR5-7 by only four amino acids and also shares significant homology with human FHR-3 and human FH SCR5-7. In contrast to FHR-1, AUC experiments indicate that FHR-B dimerization is pH-sensitive, reversible and that the monomers in the dimer present the same head to tail orientation. Mutant analyses revealed that mFH SCR5-7 also forms dimers, but less efficiently than FHR-B. Notably, substituting FHR-B Tyr162 (a key residue homologous to the disease-associated Tyr402 in human FH) for His reduces dimerization. We also found that a recombinant FHR-B with a duplicated dimerization domain formed stable dimers but lacked functional activity. Overall, FHR-B shows structural and functional similarities with various human FHRs, suggesting convergent evolution between mouse and human FHRs. Furthermore, this study reveals a novel dimerization domain shared by FHR-B and mouse FH and illustrates the importance of dimerization and monomer orientation in FHRs activity. It also underlines notable differences between human and mice FHRs that should be further explored before modeling FHR-associated human diseases in mice.
Keywords: complement; complement-related diseases; dimerization; factor H; factor-H related proteins; regulation.
Copyright © 2025 Martín-Ambrosio Doménech, González Sanz, Márquez Tirado, Juana-López, Goicoechea de Jorge, Rodríguez de Córdoba and Martín Merinero.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


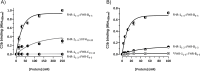


Similar articles
-
Deregulation of Factor H by Factor H-Related Protein 1 Depends on Sialylation of Host Surfaces.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 25;12:615748. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.615748. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33732239 Free PMC article.
-
Two factor H-related proteins from the mouse: expression analysis and functional characterization.Immunogenetics. 2006 Nov;58(11):883-93. doi: 10.1007/s00251-006-0153-y. Epub 2006 Oct 7. Immunogenetics. 2006. PMID: 17028856
-
Human factor H-related protein 5 has cofactor activity, inhibits C3 convertase activity, binds heparin and C-reactive protein, and associates with lipoprotein.J Immunol. 2005 May 15;174(10):6250-6. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.10.6250. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15879123
-
Recombinant generation of two fragments of the rat complement inhibitory factor H [FH(SCR1-7) and FH(SCR1-4)] and their structural and functional characterization in comparison to FH isolated from rat serum.Histol Histopathol. 2006 Jan;21(1):93-102. doi: 10.14670/HH-21.93. Histol Histopathol. 2006. PMID: 16267790 Review.
-
Complement Factor H related protein 1 and immune inflammatory disorders.Mol Immunol. 2022 May;145:43-49. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2022.03.117. Epub 2022 Mar 11. Mol Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35279539 Review.
References
-
- Hellwage J, Jokiranta TS, Koistinen V, Vaarala O, Meri S, Zipfel PF. Functional properties of complement factor H-related proteins FHR-3 and FHR-4: binding to the C3d region of C3b and differential regulation by heparin. FEBS Lett. (1999) 462:345–52. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(99)01554-9 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

