The SEPALLATA-like gene HrSEP1 in Hippophae rhamnoides regulates flower development by interacting with other MADS-box subfamily genes
- PMID: 39944949
- PMCID: PMC11813943
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1503346
The SEPALLATA-like gene HrSEP1 in Hippophae rhamnoides regulates flower development by interacting with other MADS-box subfamily genes
Abstract
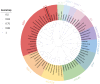
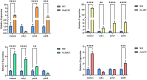
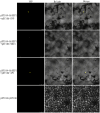
MADS-box genes are classified into five categories: ABCDE, including SEP1, SEP2, SEP3, SEP4, and other homologous genes, which play important roles in floral organ development. In this study, the cDNA sequence of the HrSEP1 gene was cloned by RT-PCR and confirmed that this gene belongs to the MADS-box gene family. In addition, subcellular localization experiments showed that the HrSEP1 protein was localized in the nucleus. We verified the interaction of HrSEP1 with HrSOC1, HrSVP, and HrAP1 using yeast two-hybrid and bimolecular fluorescence complementation assays. These genes jointly regulate the growth and development of floral organs. We also found a strong synergy between HrSEP1 and AP1 genes in sepals, petals, and stamens by transgenic methods and fluorescence quantitative PCR, suggesting that HrSEP1 and AP1 may co-regulate the development of these structures. In conclusion, the expression of HrSEP1 has a certain effect on the development of floral organs, and these findings lay the foundation for further research on the biological functions of MADS transcription factors in Hippophae rhamnoides.
Keywords: Hippophae rhamnoides; MADS-box genes; bimolecular fluorescence complementation; genetic transformation; yeast two-hybrid.
Copyright © 2025 Cong, Zhao, Ni, Li, Han, Cheng, Liu, Liu, Yao, Liu and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Functional and evolutionary analysis of the AP1/SEP/AGL6 superclade of MADS-box genes in the basal eudicot Epimedium sagittatum.Ann Bot. 2014 Mar;113(4):653-68. doi: 10.1093/aob/mct301. Epub 2014 Feb 13. Ann Bot. 2014. PMID: 24532606 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of the MADS-box gene family of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides ssp. sinensis) and their potential role in floral organ development.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Jun 13;15:1387613. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1387613. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38938643 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Three SEPALLATA-Like MADS-Box Genes Associated With Floral Development in Paphiopedilum henryanum (Orchidaceae).Front Plant Sci. 2022 May 26;13:916081. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.916081. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35693163 Free PMC article.
-
Flower development: the evolutionary history and functions of the AGL6 subfamily MADS-box genes.J Exp Bot. 2016 Mar;67(6):1625-38. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erw046. J Exp Bot. 2016. PMID: 26956504 Review.
-
The naked and the dead: the ABCs of gymnosperm reproduction and the origin of the angiosperm flower.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2010 Feb;21(1):118-28. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2009.11.015. Epub 2009 Nov 26. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 19944177 Review.
References
-
- Abdullah-Zawawi M. R., Ahmad-Nizammuddin N. F., Govender N., Harun S., Mohd-Assaad N., Mohamed-Hussein Z. A. (2021). Comparative genome-wide analysis of wrky, mads-box and myb transcription factor families in arabidopsis and rice. Sci. Rep. 11, 0–0. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-99206-y - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bai G., Yang D. H., Cao P., Yao H., Zhang Y., Chen X., et al. . (2019). Genome-wide identification, gene structure and expression analysis of the mads-box gene family indicate their function in the development of tobacco (nicotiana tabacum l.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 5043. doi: 10.3390/ijms20205043 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

