Early health technology assessment of tongue swab for non-sputum based pulmonary tuberculosis diagnosis in Thailand
- PMID: 39945002
- PMCID: PMC11814696
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lansea.2025.100533
Early health technology assessment of tongue swab for non-sputum based pulmonary tuberculosis diagnosis in Thailand
Abstract
Background: Sputum-based diagnostic methods for pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB) are challenging for patients who cannot produce sputum. Non-sputum-based approaches, such as tongue swab (TS), can address this gap. This study conducts an early Health Technology Assessment (HTA) of TS for PTB diagnosis in Thailand.
Methods: We conducted a landscape review, stakeholder consultation, early health economic modeling, and established a Target Product Profile (TPP). The landscape review included a comprehensive literature analysis to identify gaps and unmet needs in PTB diagnosis in Thailand. Stakeholder consultations gathered insights from TB experts to validate the information. An early health economic model evaluated the cost-effectiveness of two innovative strategies: tongue swab with Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) and tongue swab with real-time polymerase chain reaction (RTPCR). The TPP outlines three target levels to guide innovators in designing effective clinical studies.
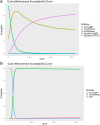
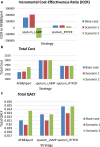
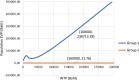
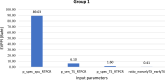
Findings: The landscape review identified the clinical workflow and reimbursement process of all PTB diagnostic tests in Thailand. The gap of tuberculosis management was around diagnosis and treatment. Stakeholders indicated that PTB detection remains inefficient due to issues such as low-test accuracy, costs, delays, drug-resistance testing, and the need for specialized laboratory techniques and personnel. TS RTPCR is the best-performing strategy, outperforming other strategies for the targeted population from the modelling analysis.
Interpretation: TS may serve as a viable alternative worth further exploration and development. An ongoing collaboration between early HTA researchers and innovators has identified valuable information for innovation development.
Funding: This work was supported by Thailand Science Research and Innovation (TSRI), Thailand, Grant Number FFB670043/0401 and Wellcome Trust grant, Grant Number 223800/Z/21/Z.
Keywords: Cost-effectiveness; Early HTA; Early health technology assessment; Economic evaluation; Economic model; Tongue swab; Tuberculosis; Tuberculosis diagnosis.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- IJzerman M.J., Steuten L.M.G. Early assessment of medical technologies to inform product development and market access: a review of methods and applications. Appl Health Econ Health Policy. 2011;9(5):331–347. - PubMed
-
- Kip M.M., Steuten L.M., Koffijberg H., IJzerman M.J., Kusters R. Using expert elicitation to estimate the potential impact of improved diagnostic performance of laboratory tests: a case study on rapid discharge of suspected non–ST elevation myocardial infarction patients. J Eval Clin Pract. 2018;24(1):31–41. - PubMed
-
- Elschot E.P., Joore M.A., Rouhl R.P.W., Lamberts R.J., Backes W.H., Jansen J.F.A. The added value of risk assessment and subsequent targeted treatment for epileptic seizures after stroke: an early-HTA analysis. Epilepsy Behav. 2024;151 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

