Effect of Initiation and Continuous Adherence to ARBs Versus ACEIs on Risk of Adjudicated Mild Cognitive Impairment or Dementia
- PMID: 39945185
- PMCID: PMC12287627
- DOI: 10.1093/gerona/glaf028
Effect of Initiation and Continuous Adherence to ARBs Versus ACEIs on Risk of Adjudicated Mild Cognitive Impairment or Dementia
Abstract
Background: Whether the differing mechanistic effects between angiotensin-2 receptor blockers (ARBs) and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) on the renin-angiotensin system translate to differential effects on clinical cognitive outcomes is unclear.
Methods: We employed an active comparator, new-user cohort study to emulate a target trial evaluating the per-protocol effect of initiating and continuously adhering to an ARB versus ACEI on adjudicated amnestic mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and probable dementia (PD) in the Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT). Inverse probability of treatment and censoring weighted cumulative incidence functions accounted for confounding, the competing risk of death, adherence, and loss to follow-up.
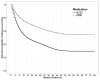
Results: Of 9,361 SPRINT participants (mean age 67.1 ± 9.5 years, 36.7% female, 58.7% non-Hispanic White), 710 and 1,289 were new users of an ARB or ACEI. Overall, 291 (41.0%) ARB initiators and 854 (66.3%) ACEI initiators were nonadherent during follow-up. The IP-weighted 4-year probabilities of full adherence and being alive among ARB was 56.0% (95% CI: 52.2%-59.9%) and 30.5% (95% CI: 28.0%-33.1%) for ACEI. The 4-year weighted risk ratios (RR) for amnestic MCI/PD and for amnestic MCI/PD/death with initiation and full adherence to ARB versus ACEI were 0.94 (95% CI: 0.66-1.29) and 0.79 (95% CI: 0.58-1.06). The weighted 4-year weighted RR for all-cause death with ARB versus ACEI initiation and adherence was 0.36 (95% CI: 0.14-0.76).
Conclusions: In this target trial emulation of older adults at high risk for cardiovascular disease, there was insufficient evidence to conclude a beneficial effect of initiating and continuously adhering to an ARB versus ACEI on adjudicated clinical cognitive outcomes.
Keywords: Antihypertensive; Cognition; Hypertension; Medication; Treatment.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Gerontological Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
-
- Livingston G, Huntley J, Sommerlad A, et al. Dementia prevention, intervention, and care: 2020 report of the Lancet commission. Lancet (London, England). 2020;396(10248):413–446. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30367-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Villapol S, Saavedra JM.. Neuroprotective effects of angiotensin receptor blockers. Am J Hypertens. 2015;28(3):289–299. https://doi.org/ 10.1093/ajh/hpu197 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Saavedra JM. Angiotensin II AT(1) receptor blockers as treatments for inflammatory brain disorders. Clin Sci (London, England : 1979). 2012;123(10):567–590. https://doi.org/ 10.1042/CS20120078 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cohen JB, Marcum ZA, Zhang C, et al. ; Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) Research Group. Risk of mild cognitive impairment or probable dementia in new users of angiotensin II receptor blockers and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(7):e2220680. https://doi.org/ 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.20680 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hernán MA, Robins JM.. Per-protocol analyses of pragmatic trials. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(14):1391–1398. https://doi.org/ 10.1056/NEJMsm1605385 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 TR003734/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL157108/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL139837/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01G065805/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG065359/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01TR003734/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG065359/American Heart Association Bugher
- U01 HL160277/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG065805/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK123104/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG055606/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG074989/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL157108/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL139837/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24DK060990/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG067497/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK060990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG055606/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AG080168/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG74989/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01-HL160277/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK123104/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL153646/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG067497/American Heart Association Bugher
- R01-HL153646/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG065805/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K24AG080168/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

