The Correlation Analysis of Factors Affecting the Effective Optical Zone After SMILE
- PMID: 39946315
- PMCID: PMC11925345
- DOI: 10.1097/ICL.0000000000001165
The Correlation Analysis of Factors Affecting the Effective Optical Zone After SMILE
Abstract
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to analyze the size of the effective optical zone (EOZ) and its related influencing factors in small incision lenticule extraction.
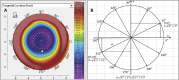
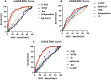
Methods: Calculation of the horizontal EOZ (Y1: H-EOZ), vertical EOZ (Y2: V-EOZ), and average EOZ (Y3: A-EOZ) using corneal topographic difference maps. Multivariate linear regression analysis was used to establish a multivariate linear equation for the dependent variable EOZ. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were constructed based on the experimental cohort and were validated in the validation cohort.
Results: The EOZ was smaller than the programmed optical zone (POZ) (p<0.001), and the spherical (Sp) and astigmatism (As) were positively correlated with H-EOZ (p Sp <0.001, p As <0.001), whereas average K-value (Km) and horizontal corneal diameter (WTW) were negatively correlated with H-EOZ (p Km <0.001, p WTW <0.002). The corresponding multivariate linear regression equation was Y1=5.246+0.168X1-0.278X2+0.027X3-0.131X4. Spherical, As, the asphericity of cornea (Q-value), and POZ were positively correlated with V-EOZ (p As <0.000, p Q <0.001, and p POZ <0.05, respectively) and Y2=3.032+0.102X1+0.175X2+0.642X5+0.415X6. Spherical, astigmatism, and POZ were positively correlated with A-EOZ (p Sp <0.000, p As <0.05, p POZ <0.05, respectively), whereas WTW was negatively correlated with A-EOZ (p WTW <0.004) as follows: Y3=4.384+0.132X1+0.023X3-0.117X4+0.294X6. The H-EOZ model had the largest area under the ROC curve, 0.853 (95% confidence interval: 0.807-0.767).
Conclusions: The preoperative intended correction of spherical lesions may be the main factor affecting the size of the postoperative EOZ, and this study has strong predictability for the horizontal EOZ.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the Contact Lens Association of Opthalmologists.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding or conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Changes of the effective optical zone after small-incision lenticule extraction and a correlation analysis.Lasers Med Sci. 2022 Dec 22;38(1):14. doi: 10.1007/s10103-022-03666-1. Lasers Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 36547739
-
Comparison of dynamic changes in the effective optical zone in Low-Moderate and high myopia with a novel method and visual outcomes after SMILE surgery: A 6-Month clinical study.Lasers Med Sci. 2025 Aug 9;40(1):331. doi: 10.1007/s10103-025-04586-6. Lasers Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40781497
-
A Comparative and Prospective Study of Corneal Consumption and Corneal Biomechanics After SMILE and FS-LASIK Performed on the Contralateral Eyes With High Myopic Astigmatism.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2024 Nov 4;13(11):29. doi: 10.1167/tvst.13.11.29. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2024. PMID: 39576656 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Methods of Corneal Vertex Centration and Evaluation of Effective Optical Zone in Small Incision Lenticule Extraction.Ophthalmic Res. 2023;66(1):717-726. doi: 10.1159/000529922. Epub 2023 Mar 14. Ophthalmic Res. 2023. PMID: 36917962 Review.
-
Astigmatism Correction Through Excimer Laser Ablation Profiles: A Descriptive Review and Guide.J Refract Surg. 2025 Aug;41(8):e855-e879. doi: 10.3928/1081597X-20250617-01. Epub 2025 Aug 1. J Refract Surg. 2025. PMID: 40778872 Review.
References
-
- Holden BA, Fricke TR, Wilson DA, et al. Global prevalence of myopia and high myopia and temporal trends from 2000 through 2050. Ophthalmology 2016;123:1036–1042. - PubMed
-
- Shah R, Shah S, Sengupta S. Results of small incision lenticule extraction: All-in-one femtosecond laser refractive surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg 2011;37:127–137. - PubMed
-
- Sekundo W, Kunert KS, Blum M. Small incision corneal refractive surgery using the small incision lenticule extraction (SMILE) procedure for the correction of myopia and myopic astigmatism: Results of a 6 month prospective study. Br J Ophthalmol 2011;95:335–339. - PubMed
-
- Seiler T, Mrochen M, Kaemmerer M. Operative correction of ocular aberrations to improve visual acuity. J Refract Surg 2000;16:S619–S622. - PubMed
-
- Wen D, Mcalinden C, Flitcroft I, et al. Postoperative efficacy, predictability, safety, and visual quality of laser corneal refractive surgery: A network meta-analysis. Am J Ophthalmol 2017;178:65–78. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

