Exploring Nursing Students' Experiences of Empathy and User Experiences in an Immersive Virtual Reality Simulation Game: Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 39946691
- PMCID: PMC11888114
- DOI: 10.2196/62688
Exploring Nursing Students' Experiences of Empathy and User Experiences in an Immersive Virtual Reality Simulation Game: Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
Background: Empathy is associated with better clinical outcomes and patient-care experiences, and it has been demonstrated that training can improve nursing students' empathy. The use of virtual reality (VR) as an experiential learning strategy may increase the empathetic behavior of caregivers. Although much research exists on the use of VR in education, there is still little research on learning empathy in nursing education through immersive VR games that include a head-mounted display and hand controllers. In addition, it is important to study both learning and user experiences in nursing education that utilizes VR technology.
Objective: This study aims to explore nursing students' experiences of empathy and user experiences in an immersive VR simulation game.
Methods: A cross-sectional design was used. A total of 52 graduating nursing students from 3 universities of applied sciences in Finland participated in the study. The immersive VR simulation game employed in the study was played with a head-mounted display and hand controllers. The instruments used were the Basic Empathy Scale in Adults (BES-A) before the VR simulation gaming session and the Comprehensive State Empathy Scale (CSES) and AttrakDiff 2.0 Scale after the session.
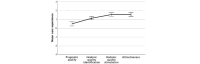
Results: The students' overall level of empathy experienced in the immersive VR simulation game was favorable (CSES; mean 2.9, SD 0.57). Participants who had a higher level of empathy (BES-A) before playing the immersive VR simulation game also experienced slightly more feelings of empathy after playing (CSES). However, the association between the measures was not statistically significant (r=0.187, P=.18). The overall empathy (CSES) experienced in the immersive VR simulation game was positively correlated with its subscales. The use of the VR simulation provided a positive user experience in all 4 factors of the AttrakDiff 2.0 Scale. Overall User Experience and Emotion Sharing correlated negatively (r=-0.248, P=.042), as did Attractiveness and Emotion Sharing (r=-0.327, P=.018). Hedonic Quality Stimulation correlated negatively with Cognitive Empathy (r=-0.279, P=.045).
Conclusions: The results of this study indicate that the use of an immersive VR simulation game in nursing education as a means of increasing empathy seems promising and justified. The immersive VR simulation game offered positive user experiences, which further supported the idea of implementing it in education. However, more research is needed on what kinds of VR environments are the most effective in promoting empathy among nursing students. Furthermore, when using VR technology in learning, one should consider that the VR setting must not be too technical but rather simple, straightforward, and predictable.
Keywords: cross sectional; education; empathy; learning; nursing; simulation; user experience; virtual reality.
©Jaana-Maija Koivisto, Sanna Kämäräinen, Katri Mattsson, Satu Jumisko-Pyykkö, Riikka Ikonen, Elina Haavisto. Originally published in JMIR Serious Games (https://games.jmir.org), 13.02.2025.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Brydon M, Kimber J, Sponagle M, MacLaine J, Avery J, Pyke L, Gilbert R. Virtual reality as a tool for eliciting empathetic behaviour in carers: an integrative review. Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Sciences. 2021 Sep;52(3):466–477. doi: 10.1016/j.jmir.2021.04.005.S1939-8654(21)00082-5 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nembhard IM, David G, Ezzeddine I, Betts D, Radin J. A systematic review of research on empathy in health care. Health Serv Res. 2023 Apr 15;58(2):250–263. doi: 10.1111/1475-6773.14016. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/35765156 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yu Chou Chuen, Tan Laurence, Tang Bernard, Liaw Sok Ying, Tierney Tanya, Ho Yun Ying, Lim Beng Eng Evelyn, Lim Daphne, Ng Reuben, Chia Siew Chin, Low James Alvin. The development of empathy in the healthcare setting: a qualitative approach. BMC Med Educ. 2022 Apr 04;22(1):245–245. doi: 10.1186/s12909-022-03312-y. https://bmcmededuc.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12909-022-03312-y 10.1186/s12909-022-03312-y - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Levett-Jones T, Lapkin S, Govind N, Pich J, Hoffman K, Jeong SY, Norton CA, Noble D, Maclellan L, Robinson-Reilly M, Everson N. Measuring the impact of a ‘point of view’ disability simulation on nursing students' empathy using the Comprehensive State Empathy Scale. Nurse Education Today. 2017 Dec;59:75–81. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2017.09.007. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

