Computational Nuclear Oncology Toward Precision Radiopharmaceutical Therapies: Current Tools, Techniques, and Uncharted Territories
- PMID: 39947910
- PMCID: PMC11960611
- DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.124.267927
Computational Nuclear Oncology Toward Precision Radiopharmaceutical Therapies: Current Tools, Techniques, and Uncharted Territories
Abstract
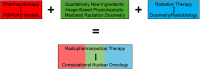
Radiopharmaceutical therapy (RPT), with its targeted delivery of cytotoxic ionizing radiation, demonstrates significant potential for treating a wide spectrum of malignancies, with particularly unique benefits for metastatic disease. There is an opportunity to optimize RPTs and enhance the precision of theranostics by moving beyond a one-size-fits-all approach and using patient-specific image-based dosimetry for personalized treatment planning. Such an approach, however, requires accurate methods and tools for the mathematic modeling and prediction of dose and clinical outcome. To this end, the SNMMI AI-Dosimetry Working Group is promoting the paradigm of computational nuclear oncology: mathematic models and computational tools describing the hierarchy of etiologic mechanisms involved in RPT dose response. This includes radiopharmacokinetics for image-based internal dosimetry and radiobiology for the mapping of dose response to clinical endpoints. The former area originates in pharmacotherapy, whereas the latter originates in radiotherapy. Accordingly, models and methods developed in these predecessor disciplines serve as a foundation on which to develop a repurposed set of tools more appropriate to RPT. Over the long term, this computational nuclear oncology framework also promises to facilitate widespread cross-fertilization of ideas between nuclear medicine and the greater mathematic and computational oncology communities.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; computational nuclear oncology; dosimetry; radiobiology; radionuclide therapy; theranostic digital twin.
© 2025 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
Figures



References
-
- Garin E, Tselikas L, Guiu B, et al. .; DOSISPHERE-01 study group. Personalised versus standard dosimetry approach of selective internal radiation therapy in patients with locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (DOSISPHERE-01): a randomised, multicentre, open-label phase 2 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;6:17–29. - PubMed
-
- Graves SA, Hobbs RF. Dosimetry for optimized, personalized radiopharmaceutical therapy. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2021;31:37–44. - PubMed
