Early Life Stress Impairs VTA Coordination of BLA Network and Behavioral States
- PMID: 39947924
- PMCID: PMC11905350
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0088-24.2025
Early Life Stress Impairs VTA Coordination of BLA Network and Behavioral States
Abstract
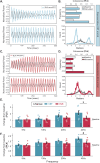
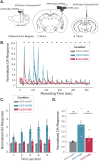
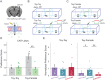
Motivated behaviors, such as social interactions, are governed by the interplay between mesocorticolimbic structures, such as the ventral tegmental area (VTA), basolateral amygdala (BLA), and medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC). Adverse childhood experiences and early life stress (ELS) can impact these networks and behaviors, which is associated with increased risk for psychiatric illnesses. While it is known that the VTA projects to both the BLA and mPFC, the influence of these inputs on local network activity which govern behavioral states-and whether ELS impacts VTA-mediated network communication-remains unknown. Our study demonstrates that VTA inputs influence BLA oscillations and entrainment of mPFC activity in mice and that ELS weakens the ability of the VTA to coordinate BLA network states, while also impairing dopaminergic signaling between VTA and BLA. Optogenetic stimulation of VTABLA terminals decreased social interaction in ELS mice, which can be recapitulated in control mice by inhibiting VTA→BLA communication. These data suggest that ELS impacts social reward via the VTA→BLA dopamine network.
Keywords: basolateral amygdala; dopamine; early life stress; oscillations; ventral tegmental area.
Copyright © 2025 Stone et al.
Figures




Update of
-
Early life stress impairs VTA coordination of BLA network and behavioral states.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Sep 17:2023.09.16.558081. doi: 10.1101/2023.09.16.558081. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: J Neurosci. 2025 Mar 12;45(11):e0088242025. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0088-24.2025. PMID: 37745617 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Sex-dependent effects of early life stress on network and behavioral states.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 10:2024.05.10.593547. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.10.593547. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Neurosci. 2025 Mar 12;45(11):e0088242025. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0088-24.2025. PMID: 38766016 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Antonoudiou P, Colmers PL, Walton NL, Weiss GL, Smith AC, Nguyen DP, Lewis M, Quirk MC, Barros L, Melon LC (2022) Allopregnanolone mediates affective switching through modulation of oscillatory states in the basolateral amygdala. Biol Psychiatry 91:283–293. 10.1016/j.biopsych.2021.07.017 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bayer SA, Altman J, Russo RJ, Zhang X (1993) Timetable of neurogenesis in the human brain based on experimentally determined patterns in the rat. Neurotoxicology 14:83–144. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
