Plasma Hepcidin as a potential informative biomarker of Alzheimer disease and vascular dementia
- PMID: 39948603
- PMCID: PMC11823057
- DOI: 10.1186/s13195-025-01696-9
Plasma Hepcidin as a potential informative biomarker of Alzheimer disease and vascular dementia
Abstract
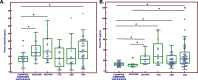
Background: Blood-based assays are expected to be integrated into clinical routines across various contexts, including Alzheimer's disease (AD). Vascular dementia (VaD), which is the second most common cause leading to dementia after AD, could also significantly benefit from this advancement. However, no informative fluid biomarker has been identified for VaD. Given the disruption of iron homeostasis in both AD and VaD, this study aims to characterize the potential of the iron-related hormone Hepcidin as a biomarker for these two conditions. We will compare its added value to established AT(N) blood biomarkers.
Methods: Blood biomarkers (amyloid-composite, p-Tau181, Neurofilament Light Chain [NfL] and Hepcidin) levels in blood were analyzed in two independent cohorts and compared between AD patients and non-AD individuals. Additionally, blood Hepcidin and NfL were evaluated in the contexts of VaD and CADASIL, with their relative diagnostic value assessed.
Results: Blood Hepcidin and NfL do not significantly increase the AUC obtained with both p-Tau181 and amyloid composite in the context of AD. In contrast, AUC for VaD diagnosis is significantly higher when combining these two blood biomarkers compared to NfL alone. Hepcidin was not significantly modified in CADASIL patients compared to control subjects.
Conclusion: Blood Hepcidin and NfL have limited interest in the clinical context of AD but determination of these biomarkers shows to be highly informative for the diagnosis of VaD. This result could have important implications for diagnosis and implementation of clinical trials.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Blood biomarkers; Diagnosis; Hepcidin; NfL; Vascular dementia.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All the patients at each clinical centre gave their written informed consent to participating in clinical research on CSF biomarkers, which was approved by the respective Ethics Committees. The committee responsible in Montpellier was the regional Ethics Committee of the Montpellier University Hospital and Montpellier CSF-Neurobank #DC-2008–417 at the certified NFS 96–900 CHU resource center BB-0033–00031, www.biobanques.eu . Authorization to handle personal data was granted by the French Data Protection Authority (CNIL) under the number 1709743 v0. Competing interests: H.Z has served at scientific advisory boards and/or as a consultant for Abbvie, Acumen, Alector, Alzinova, ALZpath, Amylyx, Annexon, Apellis, Artery Therapeutics, AZTherapies, Cognito Therapeutics, CogRx, Denali, Eisai, LabCorp, Merry Life, Nervgen, Novo Nordisk, Optoceutics, Passage Bio, Pinteon Therapeutics, Prothena, Quanterix, Red Abbey Labs, reMYND, Roche, Samumed, Siemens Healthineers, Triplet Therapeutics, and Wave, has given lectures sponsored by Alzecure, BioArctic, Biogen, Cellectricon, Fujirebio, Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Roche, and WebMD, and is a co-founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program (outside submitted work). D.A. participated in advisory boards from Fujirebio-Europe, Roche Diagnostics, Grifols S.A. and Lilly, and received speaker honoraria from Fujirebio-Europe, Roche Diagnostics, Nutricia, Krka Farmacéutica S.L., Zambon S.A.U., Neuraxpharm, Alter Medica, Lilly and Esteve Pharmaceuticals S.A. D.A. declares a filed patent application (WO2019175379 A1 Markers of synaptopathy in neurodegenerative disease). D.A. participated in advisory boards from Fujirebio-Europe, Roche Diagnostics, Grifols S.A. and Lilly, and received speaker honoraria from Fujirebio-Europe, Roche Diagnostics, Nutricia, Krka Farmacéutica S.L., Zambon S.A.U., Neuraxpharm, Alter Medica, Lilly and Esteve Pharmaceuticals S.A. D.A. declares a filed patent application (WO2019175379 A1 Markers of synaptopathy in neurodegenerative disease).
Figures



References
-
- Zecca L, Youdim MBH, Riederer P, Connor JR, Crichton RR. Iron, brain ageing and neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2004;5(11):863–73. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

