Treatment rates and delays for mental and substance use disorders: results from the Australian National Survey of Mental Health and Wellbeing
- PMID: 39949085
- PMCID: PMC11886968
- DOI: 10.1017/S2045796025000034
Treatment rates and delays for mental and substance use disorders: results from the Australian National Survey of Mental Health and Wellbeing
Abstract
Aims: Prompt initial contact with a treatment provider is a critical first step in seeking help for a mental or substance use disorders (SUDs). The aim of the current study was to provide estimates of patterns and predictors of delay in making initial treatment contact based on the recently completed Australian National Survey of Mental Health and Wellbeing.
Methods: Data came a nationally representative epidemiological survey of n = 15,893 Australians. Measures included DSM-IV lifetime diagnoses of mood (MD), anxiety (AD) and SUDs; age of disorder onset; and age of first treatment contact. Correlates of treatment delay were examined.
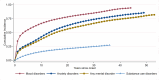
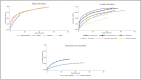
Results: SUDs exhibited the lowest lifetime treatment rate (27%), compared to MD (94%) and ADs (85%). Individuals with AD experienced the longest delay in seeking treatment (Mdn = 11 years), followed by those with SUDs (Mdn = 8 years) and MDs (Mdn = 3 years). Females had higher odds of seeking treatment for MD and AD but lower odds for SUDs. Recent birth cohorts showed increased treatment seeking across disorders, and higher education was associated with increased treatment seeking for MD and AD. Age of onset, country of birth and co-occurring disorders had mixed associations with treatment seeking.
Conclusions: The study reveals stark disparities in treatment-seeking behaviour and delays across mental and substance use disorders, with a pronounced underutilization of services for SUDs. Additionally, attention should be directed towards early intervention for individuals with earlier symptom onset, those from earlier cohorts and those with co-occurring SUDs.
Keywords: anxiety; depression; mental health; substance use; treatment delay; treatment seeking.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Delays in making initial treatment contact after the first onset of mental health disorders in the Argentinean Study of Mental Health Epidemiology.Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci. 2019 Apr;28(2):240-250. doi: 10.1017/S2045796018000094. Epub 2018 Mar 15. Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci. 2019. PMID: 29540248 Free PMC article.
-
Delay of first treatment of mental and substance use disorders in Mexico.Am J Public Health. 2007 Sep;97(9):1638-43. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2006.090985. Epub 2007 Jul 31. Am J Public Health. 2007. PMID: 17666703 Free PMC article.
-
Lifetime treatment contact and delay in treatment seeking after first onset of a mental disorder.Psychiatr Serv. 2013 Oct;64(10):981-9. doi: 10.1176/appi.ps.201200454. Psychiatr Serv. 2013. PMID: 23820725
-
Age of onset of mental disorders and use of mental health services: needs, opportunities and obstacles.Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci. 2012 Mar;21(1):47-57. doi: 10.1017/s2045796011000746. Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci. 2012. PMID: 22670412 Review.
-
[Mental health of children, adolescents and young adults--part 1: prevalence, illness persistence, adversities, service use, treatment delay and consequences].Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr. 2013 Nov;81(11):614-27. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1355843. Epub 2013 Nov 5. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr. 2013. PMID: 24194055 Review. German.
References
-
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (2024) Risky Alcohol Consumption in the NDSHS. Canberra: Australia: AIHW, Australian Government.
-
- Bischof G, Rumpf HJ, Hapke U, Meyer C and John U (2003) Types of natural recovery from alcohol dependence: A cluster analytic approach. Addiction 98(12), 1737–1746. - PubMed
-
- Borges AI and de Matos MG (2007) Substance use, mood and anxiety disorders in early adolescence. Psicologia: Teoria, Investigacao E Pratica 12(1), 73–97.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous