Risk factors and prediction model for cancer-related cognitive impairment in thyroid cancer patients
- PMID: 39949943
- PMCID: PMC11815387
- DOI: 10.62347/AOTU1301
Risk factors and prediction model for cancer-related cognitive impairment in thyroid cancer patients
Abstract
Background: Cognitive impairment is a common, yet often overlooked, complication in thyroid cancer patients, potentially influenced by various demographic, clinical, biochemical, and psychological factors. This study aims to analyze the prevalence and determinants of cancer-related cognitive impairment (CRCI) in thyroid cancer patients.
Methods: A retrospective case-control study was conducted involving 246 thyroid cancer patients treated at our The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University from January 2021 to January 2023. Patients were categorized into high cognitive function (n = 125) and low cognitive function groups (n = 121) based on Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE) scores. Data were collected on demographic variables, Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI), disease duration, clinical stage, blood test results, inflammatory factors (interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-8 (IL-8), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), C-reactive protein (CRP)), psychological status (Self-Rating Depression Scale (SDS), Self-Rating Anxiety Scale (SAS), Self-Esteem Scale (SES)), sleep quality (Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI)), and quality of life (36-item Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36)). Additionally, an external validation set was established, with patients being divided into a high cognitive level group (n = 135) and a low cognitive level group (n = 128), and the model's predictive performance was validated through the external dataset.
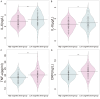
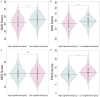
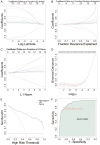
Results: Factors significantly associated with lower cognitive function included age (P < 0.001), education level (P < 0.001), CCI scores (P < 0.001), disease duration (P < 0.001), clinical stage (P = 0.003), IL-6 (P < 0.001), IL-8 (P = 0.005), TNF-α (P < 0.001) and CRP (P < 0.001). SDS (P < 0.001), SAS (P < 0.001) and PSQI (P < 0.001) were also associated with reduced cognitive function. The Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) regression model demonstrated strong predictive performance with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.903 in the training set and an AUC of 0.835 in the validation set.
Conclusion: CRCI in thyroid cancer patients is multifactorial, with significant contributions from demographic, clinical, inflammatory, and psychological factors. The developed predictive model may serve as a valuable tool in clinical practice for identifying thyroid cancer patients at high risk of cognitive impairment.
Keywords: LASSO regression; Thyroid cancer; cognitive impairment; inflammatory markers; predictive model; psychological distress.
AJCR Copyright © 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Correlation between the Degree of Inflammation and Stress Indicators and Concurrent Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Severe Craniocerebral Injury.Actas Esp Psiquiatr. 2024 Jun;52(3):317-324. doi: 10.62641/aep.v52i3.1657. Actas Esp Psiquiatr. 2024. PMID: 38863039 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological distress is involved in CRCI in breast cancer survivors via mediating cytokine levels.Cancer Med. 2023 May;12(10):11806-11815. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5847. Epub 2023 Mar 25. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 36965094 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and Predictors of Chemotherapy-Related Cognitive Impairment in Elderly Lung Cancer Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study.Brain Behav. 2025 Jun;15(6):e70594. doi: 10.1002/brb3.70594. Brain Behav. 2025. PMID: 40462671 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between inflammatory factors, lactic acid levels, acute skin failure, bad mood, and sleep quality.World J Psychiatry. 2025 Apr 19;15(4):102763. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i4.102763. eCollection 2025 Apr 19. World J Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40309608 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of cognitive impairment in patients undergoing ileostomy for colorectal cancer: a retrospective analysis.PeerJ. 2023 Jun 5;11:e15405. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15405. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37304889 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Vizer LM, Mikles SP, Piepmeier AT. Cancer-related cognitive impairment in survivors of adolescent and young adult non-central nervous system cancer: a scoping review. Psychooncology. 2022;31:1275–1285. - PubMed
-
- Larrabee K, Meeks N, Williams AM, Springer K, Siddiqui F, Chang SS, Ghanem T, Wu VF, Momin S, Tam S. Cognitive function and postoperative outcomes in patients with head and neck cancer. Laryngoscope. 2023;133:2999–3005. - PubMed
-
- Jung MS, Visovatti M, Kim M, Cha K, Dlamini N, Cui X. Cognitive impairment in women newly diagnosed with thyroid cancer before treatment. Support Care Cancer. 2022;30:8959–8967. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
