A same day α-synuclein RT-QuIC seed amplification assay for synucleinopathy biospecimens
- PMID: 39950033
- PMCID: PMC11813799
- DOI: 10.1038/s44328-024-00023-w
A same day α-synuclein RT-QuIC seed amplification assay for synucleinopathy biospecimens
Abstract
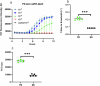
Parkinson's disease (PD), dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), and other synucleinopathies are characterized by the accumulation of abnormal, self-propagating aggregates of α-synuclein. RT-QuIC or seed amplification assays are currently showing unprecedented diagnostic sensitivities and specificities for synucleinopathies even in prodromal phases years in advance of the onset of Parkinsonian signs or dementia. However, commonly used α-synuclein seed amplification assays take ≥48 h to perform as applied to patients' diagnostic biospecimens. Here, we report the development of a faster α-synuclein RT-QuIC assay that is as analytically sensitive as prior assays of this type, but can be completed in ≤12 h for brain, skin, and intestinal mucosa, with positive signals often arising in <5 h. CSF assays took a few hours longer. Our same-day α-synuclein RT-QuIC (sdRT-QuIC) assay should increase the practicality, cost-effectiveness, and throughput of measurements of pathological forms of α-synuclein for fundamental research, clinical diagnosis, and therapeutics development.
Keywords: Biochemistry; Biological techniques; Biomarkers.
© The Authors. Parts of this work were authored by US Federal Government authors and are not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply. 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsB.C., C.O., and A.G.H. are inventors of patent applications pertaining to α-syn RT-QuIC technology. The other authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Soto, C. Unfolding the role of protein misfolding in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Rev. Neurosci.4, 49–60 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Caughey, B. & Lansbury, P. T. Jr Protofibrils, pores, fibrils, and neurodegeneration: separating the responsible protein aggregates from the innocent bystanders. Annu. Rev. Neurosci.26, 267–298 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Alam, P., Bousset, L., Melki, R. & Otzen, D. E. α‐synuclein oligomers and fibrils: a spectrum of species, a spectrum of toxicities. J. Neurochem.150, 522–534 (2019). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
