Exploring the effects of combined nostalgic activities and music therapy on Alzheimer's disease outcomes
- PMID: 39950075
- PMCID: PMC11821556
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1526761
Exploring the effects of combined nostalgic activities and music therapy on Alzheimer's disease outcomes
Abstract
Objective: Exploring the effects of combination of nostalgic activity-based therapies, including music therapy on cognitive function, negative emotions, and sleep quality in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease.
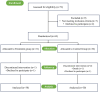
Methods: A total of 63 patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease who were treated at the Sichuan Provincial Psychiatric Center of the People's Hospital of Sichuan Province from January to June 2023 were selected as the research subjects. They were randomly divided into a study group (n = 31) and a control group (n = 32) using a random number table method. The control group received routine treatment and nursing care, while the study group received nostalgic music therapy intervention on the basis of the control group. The Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE), Montreal Cognitive Assessment Scale (MOCA), Self Rating Anxiety and Depression Scale (SAS, SDS), and Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) of the two groups were compared.
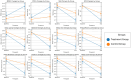
Results: A total of 30 cases from each group completed the study. After 12 weeks of intervention, the MMSE and MOCA scores of both groups of patients increased, and the treatment group was higher than the control group (P < 0.05); SAS, SDS and PSQI scores decreased compared with those before intervention, and the treatment group was lower than the control group (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Nostalgic music therapy can improve cognitive function, alleviate negative emotions, and improve sleep quality in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; cognitive function; negative emotions; nostalgic music therapy; sleep quality.
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Wang, Liu, Xiao, Huang, Zhou and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of Effect of Music and Art Combined with Kinect Game Therapy in Improving the Cognitive Function and Alleviating Negative Emotions of Alzheimer's Disease Patients in a Residential Aged Care Facilities.Altern Ther Health Med. 2024 Sep;30(9):415-419. Altern Ther Health Med. 2024. PMID: 38290446
-
[Impact of music therapy on anxiety and depression for patients with Alzheimer's disease and on the burden felt by the main caregiver (feasibility study)].Encephale. 2009 Feb;35(1):57-65. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2007.10.009. Epub 2008 Feb 20. Encephale. 2009. PMID: 19250995 French.
-
Effect of Interactive Dynamic Scalp Acupuncture on Post-Stroke Cognitive Function, Depression, and Anxiety: A Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled Trial.Chin J Integr Med. 2022 Feb;28(2):106-115. doi: 10.1007/s11655-021-3338-1. Epub 2021 Dec 7. Chin J Integr Med. 2022. PMID: 34874523 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of acupuncture for cognitive impairment in Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Dement. 2024 Jul 3;3:1380221. doi: 10.3389/frdem.2024.1380221. eCollection 2024. Front Dement. 2024. PMID: 39081600 Free PMC article.
-
Is the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) screening superior to the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) in the detection of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and Alzheimer's Disease (AD) in the elderly?Int Psychogeriatr. 2019 Apr;31(4):491-504. doi: 10.1017/S1041610218001370. Epub 2018 Nov 14. Int Psychogeriatr. 2019. PMID: 30426911
Cited by
-
A qualitative study of music-based intervention use for Alzheimer's disease in elder care communities.J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2025 Jul 29;9:25424823251363488. doi: 10.1177/25424823251363488. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2025. PMID: 40755857 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chéour S., Chéour C., Gendreau T., Bouazizi M., Singh K. P., Saeidi A., et al. . (2023). Remediation of cognitive and motor functions in Tunisian elderly patients with mild Alzheimer's disease: implications of music therapy and/or physical rehabilitation. Front. Aging Neurosci. 15:1216052. 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1216052 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources