Fixed dose combination of dapagliflozin, glimepiride and extended-release metformin tablets in patients with type 2 diabetes poorly controlled by metformin and glimepiride: A phase III, open label, randomized clinical study in India
- PMID: 39950245
- PMCID: PMC11885079
- DOI: 10.1111/dom.16218
Fixed dose combination of dapagliflozin, glimepiride and extended-release metformin tablets in patients with type 2 diabetes poorly controlled by metformin and glimepiride: A phase III, open label, randomized clinical study in India
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of a triple fixed-dose combination (FDC) therapy of dapagliflozin + glimepiride + metformin hydrochloride extended-release (DAPA + GLIM + MET ER) tablets in Indian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) inadequately controlled by combination of GLIM + MET.
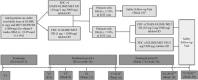
Materials and methods: A phase III, randomized, open-label, active-controlled study was conducted for a maximum 30 weeks (primary treatment [16 weeks]; uptitration [12 weeks] and follow-up [2 weeks]). Eligible patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive either the FDC of DAPA + GLIM + MET ER or the FDC of GLIM + MET prolonged-release (PR) once-daily. The primary efficacy endpoint was a change in glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) from baseline to week 16.
Results: The mean reduction in HbA1c from baseline to week 16 was significantly greater with the FDC of DAPA + GLIM + MET ER compared to the FDC of GLIM + MET PR (-1.98% ± 1.01% vs. -1.64% ± 0.86%, p = 0.0047). The mean reduction in HbA1c from baseline to week 12 was significantly greater with the FDC of DAPA + GLIM + MET ER versus dual FDC (p < 0.0001). The proportion of patients achieving HbA1c <7.0% was significantly greater with the FDC of DAPA + GLIM + MET ER versus dual FDC at week 12 (19.1% vs. 6.5%; p = 0.0002) and week 16 (52.6% vs. 36.7%; p = 0.0015). A significant decrease in HbA1c, fasting and post-prandial blood glucose from baseline to weeks 12, 16, and 28 was observed in both arms. The incidence of TEAEs was similar across both arms.
Conclusion: This study demonstrated that the FDC of DAPA + GLIM + MET ER tablets once daily was significantly better than dual FDC in achieving glycaemic control in patients with poorly controlled T2DM. Both treatments were well-tolerated.
Trial registration: CTRI/2022/03/041424, registered on 28 March 2022.
Keywords: SGLT2 inhibitor; dapagliflozin; fixed‐dose combination; glycaemic profile; metformin; type 2 diabetes.
© 2025 Sun Pharma Laboratories Limited. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors, Rakesh Sahay, Dinesh Gangwani, Manish Singh, Sandeep Gupta, Narendra Kale, Manoj Srivastava, Prakash Kurmi, Jayesh Ambaliya, Nilesh Lomte, Sandip Gofne, Saurabh Agarwal, Priyanka Kashid, Vikas Agarwal, Pradeep Rai, Surendra Sharma, L. Sreenivasa Murthy were the study investigators and they received a grant from sponsor for conducting the study at their respective sites and declare no conflict of interests. Mandodari Rajurkar, Shruti Saha, Dipak Patil, Pravin Ghadge and Suyog Mehta are full‐time employees of Sun Pharma Laboratories Ltd. Dr. Piyush Patel and Dr. Lalit Lakhwani were full‐time employees of Sun Pharma Laboratories Ltd. during the conduct of the study. Dr. Sadhna J. Joglekar was a full‐time employee of Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. during conduct of the study.
Figures



References
-
- Muralidharan S. Diabetes and current Indian scenario: a narrative review. J Diabetol. 2024;15:12‐17.
-
- Garber AJ, Abrahamson MJ, Barzilay JI, Blonde L, Bloomgarden ZT, Bush MA. Consensus statement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of endocrinology on the comprehensive type 2 diabetes management algorithm‐2016 executive summary. Endocr Pract. 2016;22:84‐113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

