Maintenance Therapy With Avelumab for Patients With Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma: A Real-World, Ambispective RAVE-Bladder Study
- PMID: 39950261
- PMCID: PMC11826084
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.70636
Maintenance Therapy With Avelumab for Patients With Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma: A Real-World, Ambispective RAVE-Bladder Study
Abstract
Background: This ambispective study was designed to assess the efficacy and safety of avelumab maintenance in a real-world population of patients with metastatic urothelial cancer (UC).
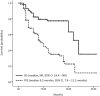
Methods: Patients with metastatic UC and measurable disease that had not progressed following first-line platinum-based chemotherapy were treated with maintenance avelumab (800 mg administered every 2 weeks). The primary endpoint was overall survival (OS).
Results: A total of 110 patients were enrolled. The majority of patients were male (81%), with a median age of 65 years (range, 36-84). The median OS was not reached, with a 1-year OS rate of 78.7%. The median PFS was 9.5 months (95% CI, 7.8-11.2 months). The ORR to first-line chemotherapy was 48.2%, and an additional 34.6% of patients responded to avelumab therapy (16 complete and 22 partial responses). Grade 3 adverse events during avelumab therapy were experienced by 11.8% of patients.
Conclusions: These findings demonstrate similar efficacy and safety of avelumab in a real-world setting when compared to data from pivotal study.
Trial registration: KCRB registry number: RAVE-Bladder.
Keywords: avelumab; maintenance therapy; metastatic urothelial carcinoma; real‐world data.
© 2025 The Author(s). Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Tsimafeyeu I. and Rahib L., “The Future Landscape of Cancer Incidence and Mortality Until 2036 in the Russian Federation,” Journal of Clinical Oncology 40, no. 16_Suppl (2022): e22518, 10.1200/JCO.2022.40.16_suppl.e22518. - DOI
-
- Tsimafeyeu I. and Tjulandin S., “First‐Line Checkpoint Inhibitors in PD‐L1‐Positive Patients With Advanced Urothelial Carcinoma,” BJU International 123, no. 4 (2019): 563–565. - PubMed
-
- Powles T., Park S. H., Voog E., et al., “Avelumab Maintenance Therapy for Advanced or Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma,” New England Journal of Medicine 383, no. 13 (2020): 1218–1230. - PubMed
-
- NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology , “Bladder Cancer,” Version 6.2024 (2025).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical