Laser-Induced Graphene from Commercial Inks and Dyes
- PMID: 39951342
- PMCID: PMC11984850
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202412167
Laser-Induced Graphene from Commercial Inks and Dyes
Abstract
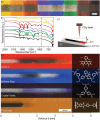
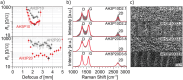
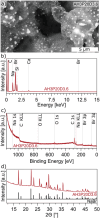
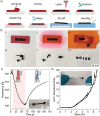
Laser-induced graphene (LIG) has been so far obtained from polymer precursors and proposed for numerous applications, including various types of sensors and energy storage solutions. This study examines a radically different class of new precursors for LIG, distinct from polymers: inks and dyes. The identification of specific organic dyes present in commercial markers demonstrates that the aromatic structure, in conjunction with high thermal stability (residual weight > 20% at 800°C), are key factors for laser-induced pyrolysis. Eosin Y is identified as an excellent LIG precursor, comparable with well-known polyimide. The unique properties of dyes allow for dispersion in various media, such as acrylic binder. A dye concentration of 0.75 mol L-1 in acrylic binder results in a conductivity of 34 ± 20 S cm-1 for LIG. The composition and microstructure of LIG from dyes are thoroughly characterized, revealing peculiar features. A versatile "Paint & Scribe" methodology is introduced, enabling to integrate LIG tracks onto any wettable surface, and in particular onto printed and flexible electronics. A process for obtaining freestanding and transferrable LIG is demonstrated by dissolving acrylic paint in acetone and floating LIG in water. This advancement offers novel avenues for diverse applications that necessitate a transfer process of LIG.
Keywords: Eosin Y; dye; freestanding; ink; laser‐induced graphene; pyrolysis; transfer.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Pinheiro T., Morais M., Silvestre S., Carlos E., Coelho J., Almeida H. V., Barquinha P., Fortunato E., Martins R., Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2402014. - PubMed
-
- Raffel J. I., Freidin J. F., Chapman G. H., Appl. Phys. Lett. 1983, 42, 705.
-
- Ge L., Hong Q., Li H., Liu C., Li F., Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1904000.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
