Hypothalamic opsin 3 suppresses MC4R signaling and potentiates Kir7.1 to promote food consumption
- PMID: 39951488
- PMCID: PMC11874419
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2403891122
Hypothalamic opsin 3 suppresses MC4R signaling and potentiates Kir7.1 to promote food consumption
Abstract
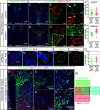
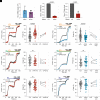
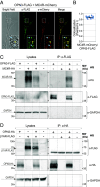
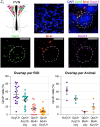
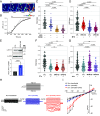
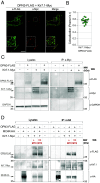
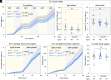
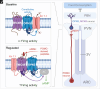
Mammalian opsin 3 (OPN3) is a member of the opsin family of G-protein-coupled receptors with ambiguous light sensitivity. OPN3 was first identified in the brain (and named encephalopsin) and subsequently found to be expressed in other tissues. In adipocytes, OPN3 is necessary for light responses that modulate lipolysis and glucose uptake, while OPN3 in human skin melanocytes regulates pigmentation in a light-independent manner. Despite its initial discovery in the brain, OPN3 functional mechanisms in the brain remain elusive. Here, we investigated the molecular mechanism of OPN3 function in the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) of the hypothalamus. We show that Opn3 is coexpressed with the melanocortin 4 receptor (Mc4r) in a population of PVN neurons, where it negatively regulates MC4R-mediated cAMP signaling in a specific and Gαi/o-dependent manner. Under baseline conditions, OPN3 via Gαi/o potentiates the activity of the inward rectifying Kir7.1 channel, previously shown to be closed in response to agonist-mediated activation of MC4R in a Gαs-independent manner. In mice, we found that Opn3 in Mc4r-expressing neurons regulates food consumption. Our results reveal the first mechanistic insight into OPN3 function in the hypothalamus, uncovering a unique mechanism by which OPN3 functions to potentiate Kir7.1 activity and negatively regulate MC4R-mediated cAMP signaling, thereby promoting food intake.
Keywords: G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR); Opsin 3 (OPN3); cAMP signaling; melanocortin 4 receptor (MC4R).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- Andrabi M., Upton B., Lang R. A., Vemaraju S., An expanding role for nonvisual opsins in extraocular light sensing physiology. Annu. Rev. Vis. Sci. 9, 245–267 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Berson D. M., Dunn F. A., Takao M., Phototransduction by retinal ganglion cells that set the circadian clock. Science 295, 1070–1073 (2002). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01EY032029/HHS | NIH | National Eye Institute (NEI)
- GRFP/NSF | NSF Graduate Research Fellowship Program (GRFP)
- R01EY027077/HHS | NIH | National Eye Institute (NEI)
- R01 EY032029/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01EY032752/HHS | NIH | National Eye Institute (NEI)
- R01 EY027077/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01EY034456/HHS | NIH | National Eye Institute (NEI)
- R01 EY032566/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01AR076241/HHS | NIH | National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS)
- R01 EY034456/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- Carney Graduate Fellowship/Brown University (BU)
- R01EY032566/HHS | NIH | National Eye Institute (NEI)
- R01 EY032752/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR076241/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- oldman Chair of the Abrahamson Pediatric Eye Institute/Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center (CCHMC)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

