Lebrikizumab vs Other Systemic Monotherapies for Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis: Network Meta-analysis of Efficacy
- PMID: 39953372
- PMCID: PMC11909319
- DOI: 10.1007/s13555-025-01357-7
Lebrikizumab vs Other Systemic Monotherapies for Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis: Network Meta-analysis of Efficacy
Abstract
Introduction: A systematic literature review and network meta-analysis (NMA) were conducted to compare the short-term efficacy of lebrikizumab to other biologic and Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor monotherapies approved for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis in adults and adolescents.
Methods: The NMA included randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled monotherapy phase 2 and 3 trials of biologics (lebrikizumab 250 mg every 2 weeks [Q2W], dupilumab 300 mg Q2W, and tralokinumab 300 mg Q2W) and JAK inhibitors (abrocitinib 100/200 mg daily, baricitinib 2/4 mg daily, and upadacitinib 15/30 mg daily) at approved doses. Efficacy outcomes included the proportions of patients achieving Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) improvement, an Investigator Global Assessment of 0 or 1 (IGA 0/1), and a ≥ 4-point improvement in pruritus/itch numeric rating scale score at 12 weeks (abrocitinib) or 16 weeks (other treatments). Itch was also assessed at week 4. A Bayesian NMA employing baseline risk-adjusted random effects models was used to estimate treatment differences.
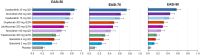
Results: Twenty-two monotherapy studies involving 8531 patients were included in the NMA. By week 12/16, lebrikizumab had superior odds of achieving IGA 0/1 and itch improvement compared to baricitinib and tralokinumab; similar odds to dupilumab, abrocitinib, and upadacitinib 15 mg; and inferior odds to upadacitinib 30 mg. Additionally, lebrikizumab had a higher probability of improving EASI than baricitinib 2 mg; similar probability to baricitinib 4 mg, tralokinumab, dupilumab, abrocitinib, and upadacitinib 15 mg; and lower probability than upadacitinib 30 mg daily. At week 4, lebrikizumab had superior odds of improving itch compared to tralokinumab; similar odds to baricitinib, dupilumab, and abrocitinib 100 mg; and inferior odds to abrocitinib 200 mg and upadacitinib.
Conclusion: Among biologics, lebrikizumab was comparable to dupilumab and superior to tralokinumab in improving response rates at week 16. Upadacitinib 30 mg was the only JAK inhibitor with superior response rates compared to lebrikizumab.
Keywords: Atopic dermatitis; Eczema Area and Severity Index; Investigator Global Assessment; Lebrikizumab; Network meta-analysis; Pruritus/itch Numeric Rating Scale.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of Interest: Jonathan I. Silverberg has served as advisor, speaker, or consultant for AbbVie, Asana Biosciences, Dermavant Sciences, Galderma, GlaxoSmithKline, Glenmark, Kiniksa, LEO Pharma, Lilly, Menlo Therapeutics, Novartis, Pfizer, Realm Pharma, and Regeneron-Sanofi and is a researcher for GlaxoSmithKline. Thomas Bieber has served as a speaker, consultant, and investigator for AbbVie, Affibody, Almirall, AnaptysBio, Arena, Asana Biosciences, ASLAN Pharmaceuticals, Bayer Health, BioVerSys, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Connect Pharma, Dermavant Sciences, Domain Therapeutics, EQRx, Galderma, Glenmark, GSK, Incyte, Innovaderm, IQVIA, Janssen, Kirin, Kymab, LEO Pharma, LG Chem, Lilly, L’Oréal, MSD, Novartis, Numab, OM Pharma, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, Q32bio, RAPT, Sanofi/Regeneron and UCB; and is the founder and chairman of the board of Davos Biosciences. Amy S. Paller has received honoraria for consulting for AbbVie, Abeona, Apogee, Arcutis, Aslan, BioCryst, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers-Squibb, Dermavant, Galderma, Incyte, Johnson and Johnson, Krystal Biotech, LEO, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Nektar, Primus, Procter and Gamble, Regeneron, Sanofi, Seanergy, TWI Biotech, and UCB. She has served as an investigator without honoraria for AbbVie, Applied Pharma Research, Dermavant, Eli Lilly, Incyte, Janssen, Krystal, Regeneron, Timber, and UCB. Lisa Beck has received grants from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, DermTech, Kiniksa, Pfizer, Regeneron, Ribon Therapeutics, and Sanofi; has received speaker’s fees or honoraria from Sanofi, Genzyme, Maruho/Galderma; has served as consultant and advisory board member for Abbvie, Allakos, Amgen, Arena Pharmaceuticals, Astra-Zeneca, Cara Therapeutics, DermTech, Escient Pharmaceuticals, Evelo Biosciences, Galderma, Genzyme, Glaxo-Smith Kline, Incyte, Invea Therapeutics, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Merck, Nektar Therapeutics, Novartis, Numab Therapeutics, Pfizer, Rapt Therapeutics, Regeneron, Ribon Therapeutics, Sanofi/Genzyme, Sanofi-Aventis, Simpson Healthcare, Stealth BioTherapeutics, Trevi Therapeutics, UCB, Union Therapeutics, and Xencor; is a member of the data monitoring committee for Novartis; and owns stocks in Gilead, Medtronic, and Moderna. Masahiro Kamata has received honoraria for lectures from AbbVie and Eli Lilly. Luis Puig has received consultancy/speaker’s honoraria from and/or participated in clinical trials sponsored by Abbvie, Almirall, Amgen, Biogen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Fresenius-Kabi, J&J Innovative Medicine, Leo-Pharma, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, STADA, Sun-Pharma, and UCB. Luis Puig, an Editorial Board member of Dermatology and Therapy, was not involved in the selection of peer reviewers for the manuscript nor any of the subsequent editorial decisions. Marni Wiseman has served as consultant, speaker, advisory board member, and clinical trial investigator for AbbVie, Amgen, Arcutis, Asana BioSciences, AstraZeneca, Bausch Health, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Dermira, Eli Lilly, Galderma, Glenmark, Incyte, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Principia, PRCL Research, Regeneron, Sanofi, UCB, and La Roche-Posay. Khaled Ezzedine has received consulting fees from AbbVie, Incyte, La Roche-Posay, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, Sanofi, MSD, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Almirall. Alan D. Irvine is a consultant and/or advisory board member and/or is on the Data Safety Monitoring Board for: AbbVie, Almirall, Arena Pharmaceuticals, BenevolentAI, Eli Lilly and Company, LEO Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi; has received research grants from: AbbVie and Pfizer; is on the board of directors of: the International Eczema Council; provides research support to: Regeneron; and is on the speaker’s bureau for: AbbVie, Eli Lilly and Company, Regeneron, and Sanofi Genzyme. Peter Foley has received grants from AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Galderma, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, Sun Pharma, and UCB Pharma; has served as an investigator for AbbVie, Amgen, Argenx, Arcutis, Aslan, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Botanix, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Celtaxsys, CSL, Cutanea, Dermira, Eli Lilly, Evelo, Galderma, Genentech, Geneseq, GlaxoSmithKline, Hexima, Incyte, Janssen, Kymab, LEO Pharma, Merck, MedImmune, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Reistone, Roche, Sanofi, Sun Pharma, Teva, UCB, and Valeant; has served as advisory board member for AbbVie, Amgen, Aslan, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Galderma, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Mayne Pharma, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, Sun Pharma, UCB, and Valeant; has served as a consultant for Aslan, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Galderma, GenesisCare, Hexima, Janssen, LEO Pharma, MedImmune, Mayne Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB; has received travel grants from AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Galderma, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sun Pharma, and Sanofi; and has received speaker’s fees or honoraria from AbbVie, Amgen, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Galderma, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, Sun Pharma, and Valeant. James Del Rosso has received grants as an investigator, honoraria for lecturing, and/or consulting fees from AbbVie, Amgen (Celgene), AOBiome, Aslan, Arbonne, Arcutis, Bausch Health (Ortho Derm), Bristol Myers Squibb, Dermavant, Dermira, Eli Lilly and Company, Exeltis, Ferndale, Galderma, Incyte, IntraDerm, Johnson & Johnson, La Roche-Posay/L’Oréal, LEO Pharma, Menlo Therapeutics, Nektar, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, Regeneron/Sanofi Genzyme, Sun Pharma, Theraplex, UCB Pharma, Unilever, and Verrica Pharmaceuticals. Linda Stein Gold is an investigator and/or consultant and/or speaker for: AbbVie, Amgen, Arcutis, Bristol Myers Squibb, Dermavant, Eli Lilly and Company, Galderma, Incyte Corporation, Janssen, Novartis, Ortho Dermatologics, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, and UCB Pharma. Erin Johansson, Martin Dossenbach, Gaia Gallo, and Marta Casillas are employees and minor shareholders of Eli Lilly and Company, which funded this study. Buelent Akmaz is an employee of Almirall. Andrei Karlsson and Tristan Curteis are employees of Costello Medical, which was funded by Eli Lilly and Company to provide analytical services for this publication. Raj Chovatiya served as an advisor, consultant, speaker, and/or investigator for AbbVie, Amgen, Apogee Therapeutics, Arcutis, Argenx, ASLAN Pharmaceuticals, Beiersdorf, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Cara Therapeutics, Dermavant, Eli Lilly and Company, FIDE, Galderma, Genentech, GSK, Incyte, LEO Pharma, L’Oréal, Nektar Therapeutics, Novartis, Opsidio, Pfizer Inc., Regeneron, RAPT, Sanofi, Sitryx, and UCB. Ethical Approval: This study is based on previously conducted studies and does not contain any new studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Figures




References
-
- Avena-Woods C. Overview of atopic dermatitis. Am J Manag Care. 2017;23(8 Suppl):S115–23. - PubMed
-
- Ständer S, Simpson EL, Guttman-Yassky E, et al. Clinical relevance of skin pain in atopic dermatitis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2020;19(10):921–6. 10.36849/jdd.2020.5498. - PubMed
-
- Nutten S. Atopic dermatitis: global epidemiology and risk factors. Ann Nutr Metab. 2015;66(Suppl 1):8–16. 10.1159/000370220. - PubMed
-
- Augustin M, Misery L, von Kobyletzki L, et al. Unveiling the true costs and societal impacts of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis in Europe. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022;36(Suppl 7):3–16. 10.1111/jdv.18168. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

