HER2-low status as a distinct breast cancer subtype: myth or truth? Analysis of the WSG trials WSG-ADAPT-HR+/HER2-, WSG-PlanB, and WSG-ADAPT-TN
- PMID: 39953511
- PMCID: PMC11827153
- DOI: 10.1186/s13058-025-01969-z
HER2-low status as a distinct breast cancer subtype: myth or truth? Analysis of the WSG trials WSG-ADAPT-HR+/HER2-, WSG-PlanB, and WSG-ADAPT-TN
Abstract
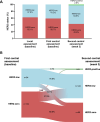
Background: New data show that not only HER2-overexpressing breast cancer (BC) tumors but also HER2-low tumors, classically considered as HER2-negative, respond to HER2-targeting antibody-drug-conjugates. Our objective was to analyze the prevalence of HER2-low BC in a pooled analysis of contemporary early BC trials and to evaluate its role as a prognostic factor in terms of survival in comparison to HER2-zero BC.
Methods: We evaluated 5598 patients with locally HR + /HER2- BC from the screening cohort of WSG-ADAPT-HR + /HER2-, 2592 patients with HR + /HER2- or HR-/HER2- from the adjuvant WSG-PlanB trial, and 336 patients from the WSG-ADAPT-TN trial. Central HER2 testing was performed prospectively in WSG-ADAPT and retrospectively in WSG-PlanB. Following ASCO/CAP guidelines, HER2-low status was defined as immunohistochemistry (IHC) 1 + or 2 + and in situ hybridization (ISH)-negative, and HER2-zero was defined as IHC 0. Agreement between HER2 assessments was evaluated with Cohen's kappa coefficient, and effects of HER2 status on pathological complete response (pCR) and on survival were analyzed with logistic regression and Cox proportional hazards models, respectively.
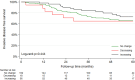
Findings: In WSG-ADAPT-HR + /HER2-, 3198 (64.6%) tumors were HER2-low by the central and 3096 (55.6%) by the local histology (agreement for HER2-low status was 61.0%). In HR + /HER2- cases from WSG-PlanB, 601 tumors (28.7%) were HER2-low. In both cohorts, HER2-low status was significantly associated with higher ERBB2 mRNA expression by Oncotype DX test in comparison to HER2-zero: mean 9.3 vs. 9.1 (p < .001) by local HER2 assessment in WSG-ADAPT and mean 9.2 vs. 8.8 (p < .001) in WSG-PlanB. Furthermore, patients with HER2-low tumors in WSG-ADAPT-HR + /HER2- significantly less often had a pCR compared to the HER2-zero tumors (p = .015). No significant difference was observed in (invasive and/or distant) disease-free survival (DFS) between centrally HER2-low and HER2-zero tumors in both HR + /HER2- cohorts (WSG-ADAPT-HR + /HER2- distant DFS: unadjusted HR = 1.06, 95%CI 0.83-1.36, similar results for local assessment; WSG-PlanB DFS: unadjusted HR = 1.28, 95%CI 0.91-1.82). In the HR-/HER2- WSG-PlanB cohort, centrally HER2-low tumors (10.5%) were associated with better DFS (unadjusted HR = 0.21, 95%CI 0.05-0.83), this association was not observed in the WSG-ADAPT-TN.
Conclusion: The prevalence of HER2-low status varied between the analyzed trials. Our results show that survival does not differ between HER2-low and HER2-zero tumors in HR + /HER2- cohorts; however, HER2-low status appears to have an inconsistent impact on survival in TNBC. Therefore, our findings do not support the characterization of HER2-low status as a distinct BC subtype.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: WSG-ADAPT und PlanB trials were approved by institutional ethic boards and ethic committees, and national authorities and were conducted according to Declaration of Helsinki. All patients have signed consent to participate. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.Supplementary
Figures

References
-
- Board WHOCWHOCTE, Cancer IAfRo: WHO Classification of Breast Tumours: WHO Classification of Tumours, Volume 2: World Health Organization; 2019.
-
- Rojas K, Stuckey A. Breast cancer epidemiology and risk factors. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2016;59(4):651–72. - PubMed
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

