TREM2 Depletion in Pancreatic Cancer Elicits Pathogenic Inflammation and Accelerates Tumor Progression via Enriching IL-1β+ Macrophages
- PMID: 39956331
- PMCID: PMC12103993
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.01.244
TREM2 Depletion in Pancreatic Cancer Elicits Pathogenic Inflammation and Accelerates Tumor Progression via Enriching IL-1β+ Macrophages
Abstract
Background & aims: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) has a complex tumor microenvironment enriched with tumor-associated macrophages. Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2) is highly expressed by a subset of macrophages in PDAC. However, the functional role of TREM2 in PDAC progression remains elusive.
Methods: We generated a novel transgenic mouse model (KPPC;Trem2-/-) that enables the genetic depletion of TREM2 in the context of spontaneous PDAC development. Single-cell RNA-sequencing analysis was used to identify changes in the tumor immune microenvironment on TREM2 depletion. We evaluated the impacts of TREM2 depletion on the tumor immune microenvironment to elucidate the functions of TREM2 in macrophages and PDAC development.
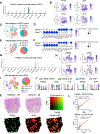
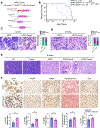
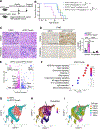
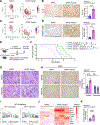
Results: Unexpectedly, genetic depletion of TREM2 significantly accelerated spontaneous PDAC progression and shortened the survival of KPPC;Trem2-/- mice. Single-cell analysis revealed that TREM2 depletion enhanced proinflammatory macrophages and exacerbated pathogenic inflammation in PDAC. Specifically, TREM2 functions as a key braking mechanism for the NLRP3/nuclear factor-κB/interleukin (IL)-1β inflammasome pathway, opposing to microbial lipopolysaccharide as the key activator of this pathway. TREM2 deficiency orchestrated with microbial lipopolysaccharide to trigger IL-1β upregulation and pathogenic inflammation, thereby fueling PDAC development. Notably, IL-1β inhibition or microbiome ablation not only reversed the accelerated PDAC progression caused by TREM2 depletion, but also further inhibited PDAC progression in the TREM2-depleted context.
Conclusions: TREM2 depletion accelerates tumor progression by enhancing proinflammatory macrophages and IL-1β-mediated pathogenic inflammation in PDAC. The accelerated tumor progression by TREM2 depletion can be reversed by blocking IL-1β-associated pathogenic inflammation.
Keywords: Genetically Engineered Mouse Models; Macrophages; Pancreatic Cancer; Single-Cell RNA-Sequencing; TREM2; Tumor Immune Microenvironment.
Copyright © 2025 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

