Coeliac disease masquerading as macroamylasaemia
- PMID: 39956571
- PMCID: PMC11831057
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2024-262400
Coeliac disease masquerading as macroamylasaemia
Abstract
Macroamylasaemia (MA) is a biochemical disorder characterised by elevated serum amylase activity, resulting from the circulation of a macromolecular complex of amylase bound to a serum component, often an immunoglobulin. The increased molecular weight of this complex prevents the normal renal excretion of the enzyme. A few cases of adult patients with coeliac disease (CD) and MA have been reported, in which the biochemical disorder resolved after treatment with a gluten-free diet. However, in other cases, this resolution did not occur. Here, we report a case of CD masquerading as recurrent pancreatitis due to the presence of MA.
Keywords: Coeliac disease; Gastrointestinal system; Small intestine.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
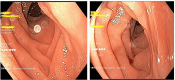
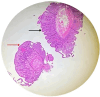
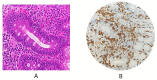
References
-
- Šimac D, Šimac M, Devčić B, et al. Diagnosing Macroamylasemia in Unexplained Hyperamylasemia. Acta Med Croatica. 2017;71:63–6.
-
- Pieper-Bigelow C, Strocchi A, Levitt MD. Where does serum amylase come from and where does it go? Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1990;19:793–810. - PubMed
-
- Sturk A, Sanders GT. Macro enzymes: prevalence, composition, detection and clinical relevance. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1990;28:65–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
