The economic impact of stent retriever selection for acute ischemic stroke: a cost analysis of MASTRO I from the healthcare system perspective of the United States, Canada and eight European countries
- PMID: 39957470
- PMCID: PMC11864083
- DOI: 10.57264/cer-2024-0216
The economic impact of stent retriever selection for acute ischemic stroke: a cost analysis of MASTRO I from the healthcare system perspective of the United States, Canada and eight European countries
Abstract
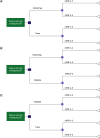
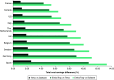
Aim: According to the results of the MASTRO I living systematic review and meta-analysis, use of the EmboTrap Revascularization® Device in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke (AIS) results in higher rates of good functional outcomes (90-day modified Rankin Scale [mRS] 0-2) compared with use of the Trevo® Retriever or the Solitaire™ Revascularization Device. The aim of this analysis was to assess the potential economic impact of achieving improved functional outcomes for three commonly used stent retrievers (SRs) in the treatment of AIS. Methods: An economic model with short-term and long-term costs, representing a healthcare system perspective was developed using a decision tree to simulate a cohort of 1000 hypothetical patients treated for AIS with mechanical thrombectomy (MT) using EmboTrap, Trevo or Solitaire SRs. Based on the proportion of patients who achieved a 90-day mRS score of 0-2 or 3-5 for each device reported in MASTRO I (excluding patients not surviving after 90 days), this model estimated per-patient costs and the associated incremental cost savings. Results are reported from the healthcare system perspective in the US, Canada, the UK, Sweden, Germany, France, Italy, Spain, Belgium and The Netherlands. Results: Across all ten countries, the use of EmboTrap during MT was associated with the lowest short-term (ranging from €8412 in Italy to $66,525 in the US), long-term (ranging from €5249 in Italy to $25,757 in the US) and total (ranging from €13,661 in Italy to $92,282 in the US) per-patient costs. The total per-patient cost was higher with Trevo (ranging from €14,601 in Italy to $97,487 in the US) and Solitaire (ranging from €14,840 in Italy to $98,814 in the US). Cost savings were highest when comparing EmboTrap versus Solitaire, followed by EmboTrap versus Trevo, with Trevo versus Solitaire having the smallest cost savings. Results of sensitivity and scenario analyses supported the robustness of the base-case results. Conclusion: Across the ten countries, treating patients with AIS with EmboTrap resulted in lower short-term, long-term and total costs to the payer. With rising healthcare costs and limited hospital budgets, these results suggest EmboTrap proves to be an evidence-based economical choice of SR for hospitals and healthcare systems.
Keywords: EmboTrap; MASTRO I; Solitaire; Trevo; acute ischemic stroke; cost; economic; mechanical thrombectomy; modified Rankin Scale; stent retriever.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
Competing interests disclosure
T Andersson reports consulting fees for Anaconda, Johnson & Johnson MedTech, Neuravi, Rapid Medical, Optimize Neurovascular and holds equity in Ceroflo. H Nordmeyer reports consulting fees from Acandis, Balt, Johnson & Johnson MedTech, Rapid Medical. W Brinjikji reports consulting fees for Medtronic, Stryker, Imperative Care, Microvention, MIVI Neurovascular, Johnson & Johnson MedTech, Asahi, and Balt; holds equity in Nested Knowledge, Superior Medical Editors, Piraeus Medical, Sonoris Medical, and MIVI Neurovascular; receives royalties from Medtronic and Balloon Guide Catheter Technology; and serves in a leadership or fiduciary role for MIVI Neurovascular, Marblehead Medical LLC, Interventional Neuroradiology (Editor in Chief), Piraeus Medical, and WFITN. E Kottenmeier, M Kabiri, S Scheffler, PA Brouwer, M Mirza all report employment by Johnson & Johnson MedTech. OO Zaidat reports consulting fees for Stryker, Medtronic, Johnson & Johnson MedTech, and Penumbra; research grants from Stryker, Medtronic, Johnson & Johnson MedTech, Penumbra, and Genentech; in addition, OO Zaidat had a patent for ischemic stroke issued. The authors have no other competing interests or relevant affiliations with any organization/entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
The authors have no other competing interests or relevant affiliations with any organization/entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The economic impact associated with stent retriever selection for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke: a cost-effectiveness analysis of MASTRO I data from a Chinese healthcare system perspective.J Comp Eff Res. 2024 Nov;13(11):e240160. doi: 10.57264/cer-2024-0160. Epub 2024 Nov 5. J Comp Eff Res. 2024. PMID: 39498634 Free PMC article.
-
MASTRO I: Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review of thrombectomy stent retriever outcomes: comparing functional, safety and recanalization outcomes between EmboTrap, Solitaire and Trevo in acute ischemic stroke.J Comp Eff Res. 2023 May;12(5):e230001. doi: 10.57264/cer-2023-0001. Epub 2023 Apr 11. J Comp Eff Res. 2023. PMID: 37039285 Free PMC article.
-
Solitaire Stentectomy Using a Stent-Retriever Technique in a Porcine Model.Clin Neuroradiol. 2021 Jun;31(2):475-482. doi: 10.1007/s00062-020-00906-1. Epub 2020 May 18. Clin Neuroradiol. 2021. PMID: 32424667 Free PMC article.
-
Primary Results of the Multicenter ARISE II Study (Analysis of Revascularization in Ischemic Stroke With EmboTrap).Stroke. 2018 May;49(5):1107-1115. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.020125. Epub 2018 Apr 11. Stroke. 2018. PMID: 29643261
-
North American Solitaire Stent Retriever Acute Stroke registry: post-marketing revascularization and clinical outcome results.J Neurointerv Surg. 2018 Jul;10(Suppl 1):i45-i49. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2013-010895.rep. J Neurointerv Surg. 2018. PMID: 30037956
Cited by
-
Cost impact of balloon guide catheter with mechanical thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke: Analysis from the United States, Canada, and seven European countries.Interv Neuroradiol. 2025 Jul 24:15910199251359730. doi: 10.1177/15910199251359730. Online ahead of print. Interv Neuroradiol. 2025. PMID: 40702882 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tsao CW, Aday AW, Almarzooq ZI et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2023 Update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 147(8), e93–e621 (2023). - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. The top 10 causes of death. (Accessed: February 2024). https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of...
-
- Cruz Martínez MY, Alejandra Cantú Saldaña K, Antonio Ibarra Arias JJ. Available therapeutics after a stroke: current and promising options. New Insight into Cerebrovascular Diseases - An Updated Comprehensive Review (2020).
-
- Gbiri CA, Olawale OA, Isaac SO. Stroke management: informal caregivers' burdens and strians of caring for stroke survivors. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 58(2), 98–103 (2015). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
