Comparative analysis of anaesthesia modalities in pulmonary vein isolation: insights from a prospective multicentre registry
- PMID: 39957475
- PMCID: PMC11831030
- DOI: 10.1093/europace/euae301
Comparative analysis of anaesthesia modalities in pulmonary vein isolation: insights from a prospective multicentre registry
Abstract
Aims: Atrial fibrillation (AF), the most common sustained arrhythmia in adults, is increasing in prevalence globally. Catheter ablation (CA), particularly pulmonary vein isolation (PVI), is a key treatment option. Pulmonary vein isolation can be performed using different energy sources, including cryoballoon ablation (CBA), radiofrequency ablation (RFA), or pulse field ablation. Anaesthesia modalities for these procedures include general anaesthesia (GA), deep sedation (DS), and conscious sedation (CS). However, the optimal anaesthesia modality remains unclear, as previous studies have shown mixed outcomes. This study aims to compare the safety and efficacy of different anaesthesia modalities in PVI.
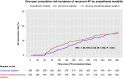
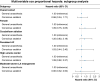
Methods and results: This prospective, multicentre study, based on the Israeli Catheter Ablation Registry, evaluated the impact of different anaesthesia modalities on procedural outcomes and safety in AF ablation. Data from 1002 patients who underwent PVI between January 2019 and December 2021 across 14 centres were analysed. Patients were stratified by anaesthesia modality-CS vs. GA, with the latter encompassing DS. Key outcomes, including AF recurrence, procedural complications, and success rates, were evaluated over a 24-month follow-up period. Additionally, a sensitivity analysis was performed for the subgroup of patients who underwent CBA. Of the 1002 patients, 53% received GA, 6.3% DS, and 40% CS, with CBA used in 84% of cases. Complete PVI was achieved in 91% of patients, with comparable success rates observed between CS and GA groups. No significant differences were found between CS and GA modalities in terms of AF recurrence rates at 12 months (15% vs. 16%) and 24 months (19.5% vs. 21.2%), or in 12-month rehospitalization rates (19.8% vs. 16.5%). Sensitivity analysis of the CBA subgroup yielded similar results, with no significant differences in AF recurrence, complications, or procedural duration between CS and GA modalities.
Conclusion: Conscious sedation is as safe and effective as general anaesthesia in AF ablation, particularly with cryoablation. The choice of anaesthesia appears to be driven by patient characteristics and institutional factors without affecting long-term outcomes such as AF recurrence or complication rates.
Keywords: AF recurrence; Conscious sedation; Cryoballoon ablation; General anaesthesia; Pulmonary vein isolation; Radiofrequency ablation.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: none declared.
Figures

References
-
- Tsao CW, Aday AW, Almarzooq ZI, Anderson CAM, Arora P, Avery CL et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2023 Update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2023;147:e93–621. - PubMed
-
- Rahman F, Kwan GF, Benjamin EJ. Global epidemiology of atrial fibrillation. Nat Rev Cardiol 2014;11:639–54. - PubMed
-
- Van Gelder IC, Rienstra M, Bunting KV, Casado-Arroyo R, Caso V, Crijns HJGM et al. 2024 ESC guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur Heart J 2024;45:ehae176.36. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin EJ, Levy D, Vaziri SM, D’Agostino RB, Belanger AJ, Wolf PA. Independent risk factors for atrial fibrillation in a population-based cohort. JAMA 1994;271:840–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

