Associations of Cerebrospinal Fluid Orexin-A, Alzheimer Disease Biomarkers, and Cognitive Performance
- PMID: 39957622
- PMCID: PMC12040502
- DOI: 10.1002/acn3.70009
Associations of Cerebrospinal Fluid Orexin-A, Alzheimer Disease Biomarkers, and Cognitive Performance
Abstract
Objective: Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) orexin-A has been suggested to be a biomarker of Alzheimer disease (AD). In both cognitively unimpaired healthy older adults and individuals with symptomatic AD, CSF orexin-A is positively associated with CSF Aβ42, p-tau181, and total tau (t-tau) concentrations. However, a recent systematic review and meta-analysis did not support differences in orexin-A between AD and controls. In this study, we tested the association between CSF orexin-A concentrations, AD biomarkers, and cognitive performance in older adults with and without symptomatic AD.
Methods: Two hundred and seventy community-dwelling older adults underwent standardized cognitive assessments, sleep monitoring with a single-channel electroencephalography test, one night of home sleep apnea testing, biofluid and imaging AD biomarker measurement within 1 year of sleep monitoring, and APOE genotyping. Plasma and CSF AD biomarkers were measured by immunoassay or mass spectrometry. CSF orexin-A was measured by radioimmunoassay.
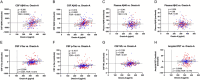
Results: CSF orexin-A levels did not differ by amyloid positivity, cognitive status, or AD stage. However, CSF AD biomarkers (Aβ40, Aβ42, and t-tau) were positively associated with CSF orexin-A levels even after correction for multiple comparisons. CSF orexin-A was not associated with any measure of cognitive performance.
Interpretation: This study showed that CSF orexin-A is associated with multiple CSF AD biomarkers, but not with AD pathology or cognitive performance. We hypothesize that this is due to similar mechanisms of production/release of these proteins with sleep-wake activity. Future studies measuring other forms of orexin peptides, such as orexin-B, may provide evidence for orexin as a marker for AD.
© 2025 The Author(s). Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
R.L., K.S., C.D.T., A.H., R.R., S.F., and C.X. report no conflicts. E.M. receives consulting fees from Takeda Pharmaceuticals and owns equity in Centessa, companies involved in the development of orexin agonists. He is an investigator of research contracts or funded clinical trials sponsored by Avadel, Alkermes, Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Eisai, Jazz Pharmaceuticals and Vanda. S.E.S. has served on advisory boards or received honoraria for presentations for Eisai, Eli Lilly, and Novo Nordisk. T.L.S.B. reports research support from Siemens; consulting fees from Biogen, Eli Lilly, Eisai, Bristol Myers Squibb, Johnson and Johnson, and Merck; honoraria from Medscape and PeerView; participation in Data Safety Monitoring Boards or Advisory Boards for Eisai and Siemens. J.H. receives consulting fees for AlzPath and Prothena. J.C.M. is funded by NIH grants P30 AG066444, P01 AG003991, and P01 AG026276. Neither Dr. Morris nor his family owns stock or has equity interest (outside of mutual funds or other externally directed accounts) in any pharmaceutical or biotechnology company. D.M.H. is an inventor on a patent licensed by Washington University to NextCure on the therapeutic use of anti‐ApoE antibodies. DMH cofounded, has equity in, and is on the scientific advisory board of C2N Diagnostics. DMH is on the scientific advisory boards of Denali, Genentech, and Cajal Neuroscience and consults for Asteroid and Switch Therapeutics. B.P.L. receives consulting fees from Eisai, Eli Lilly, and the Weston Family Foundation. BPL serves on Data Safety and Monitoring Boards for Eli Lilly. BPL serves on the Scientific Advisory Board for Beacon Biosignals. BPL receives drug/matched placebo from Merck for a clinical trial funded by a private foundation and drug/matched placebo from Eisai for a clinical trial funded by the NIA. Washington University has a financial interest in C2N Diagnostics.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

