Long-term hepatitis B surface antigen kinetics after nucleos(t)ide analog discontinuation in patients with noncirrhotic chronic hepatitis B
- PMID: 39957751
- PMCID: PMC11771267
- DOI: 10.1016/j.livres.2024.07.001
Long-term hepatitis B surface antigen kinetics after nucleos(t)ide analog discontinuation in patients with noncirrhotic chronic hepatitis B
Abstract
Background and aim: Few studies have reported hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) kinetics after nucleos(t)ide analog (NA) discontinuation in patients with noncirrhotic chronic hepatitis B (CHB). The study specifically investigated long-term HBsAg kinetics after NA discontinuation.
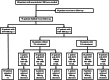
Methods: Between January 2014 to January 2024, this study prospectively enrolled 106 outpatients with noncirrhotic CHB who met the discontinuation criteria after NA consolidation treatment. Demographic, clinical, and laboratory data were collected and analyzed after NA discontinuation.
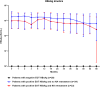
Results: Ninety-six patients who finished 5 years of follow-up were included. HBsAg remained undetectable in 29 patients with end of treatment (EOT) HBsAg negativity. Among 67 patients with EOT HBsAg positivity, HBsAg seroclearance occurred in 12 (17.9%) patients with an estimated annual incidence of HBsAg seroclearance of 3.6%. Patients with EOT HBsAg levels of ≤1000 IU/mL had a higher HBsAg seroclearance rate than those with EOT HBsAg levels of >1000 IU/mL (33.3% vs. 5.4%). The proportion of patients with HBsAg ≤1000 IU/mL increased during follow-up. Logistic regression analysis indicated that the EOT HBsAg level was an independent factor for HBsAg seroclearance and an HBsAg level decline exceeding 1 log10 IU/mL. The optimal EOT HBsAg cutoff for both HBsAg seroclearance and an HBsAg level decline exceeding 1 log10 IU/mL was 359 IU/mL.
Conclusions: Patients with EOT HBsAg negativity experienced no relapse and maintained HBsAg seroclearance during 5 years of follow-up after NA discontinuation. A higher HBsAg seroclearance rate can be obtained in patients with EOT HBsAg levels of ≤1000 IU/mL during 5 years of follow-up after NA discontinuation. Close monitoring and proper NA retreatment are recommended to guarantee the safety of NA discontinuation.
Clinical trial number: Clinicaltrials.gov number NCT02883647.
Keywords: Chronic hepatitis B (CHB); Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg); Hepatitis B virus (HBV); Kinetics; Nucleos(t)ide analogs (NAs); Quantitative HBsAg.
© 2024 The Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University. Publishing services by Elsevier B. V. on behalf of KeAi Communications Co. Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Zhiliang Gao is an associate editor for Liver Research and was not involved in the editorial review or the decision to publish this article. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization . World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2017. Global Hepatitis Report, 2017.https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/global-hepatitis-report-2017
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
