The Effect of Exosomes Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells on the Regeneration of Human Pulpectomized Tooth: A Case Report
- PMID: 39957811
- PMCID: PMC11829066
- DOI: 10.30476/ijms.2024.103117.3638
The Effect of Exosomes Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells on the Regeneration of Human Pulpectomized Tooth: A Case Report
Abstract
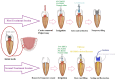
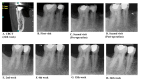
The dental pulp is essential for tooth health and sensory function. However, conventional treatments for infected or necrotic pulp, such as root canal therapy, frequently result in tooth loss and increased fracture risk. Regenerative endodontic procedures (REPs) aim to regenerate pulp tissue while preserving tooth vitality. Exosomes from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal/stem cells (hUCMSCs) demonstrated potential for tissue regeneration. In this case report, the potential of hUCMSC-derived exosomes for regenerating the dental pulp of a pulpectomized tooth was investigated. The patient, a 40-year-old man, was presented with irreversible pulpitis in the mandibular second premolar. The patient underwent a pulpectomy, followed by the application of a chitosan and hUCMSC-derived exosome mixture into the root canal. This project was conceived and executed as a joint project in Bushehr (Iran), Shiraz (Iran), and Aktobe (Kazakhstan) from 2022 to 2024. Exosomes were isolated and characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Clinical evaluations, including visual inspection, palpation, pulp vitality tests, radiography, and cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) imaging, were conducted over 24 weeks post-treatment. The SEM and TEM images confirmed the effective isolation and characterization of exosomes. Clinical follow-ups showed no signs of infection, swelling, or tenderness around the treated tooth. Radiographic assessments indicated periapical radiolucency and periodontal ligament widening, suggesting active healing. Despite these radiographic changes, the absence of clinical symptoms indicated successful tissue regeneration and integration. This case report demonstrated the potential of hUCMSC-derived exosomes for dental pulp regeneration, with promising results in maintaining tooth vitality and promoting healing.
Keywords: Dental pulp; Exosomes; Mesenchymal stem cells; Regeneration; Regenerative endodontics.
Copyright: © Iranian Journal of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflict of interest as some of the authors are affiliated with PerciaVista R&D Co., Iran, the manufacturer of the Exovista kit used in this study. This affiliation could be perceived as a potential source of bias; however, the authors affirmed that all efforts were made to ensure objectivity and integrity in the conduct of the research, analysis of data, and reporting of results.
Figures

References
-
- Kwack KH, Lee HW. Clinical Potential of Dental Pulp Stem Cells in Pulp Regeneration: Current Endodontic Progress and Future Perspectives. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:857066. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.857066. [ PMC Free Article ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhuang X, Ji L, Jiang H, Liu Y, Liu X, Bi J, et al. Exosomes Derived from Stem Cells from the Apical Papilla Promote Dentine-Pulp Complex Regeneration by Inducing Specific Dentinogenesis. Stem Cells Int. 2020;2020:5816723. doi: 10.1155/2020/5816723. [ PMC Free Article ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chetty S, Yarani R, Swaminathan G, Primavera R, Regmi S, Rai S, et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells-from bench to bedside. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:1006295. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1006295. [ PMC Free Article ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Long R, Wang S. Exosomes from preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells: Tissue repair and regeneration. Regen Ther. 2024;25:355–66. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2024.01.009. [ PMC Free Article ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
