MUTYH is a potential prognostic biomarker and correlates with immune infiltrates in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 39957908
- PMCID: PMC11791856
- DOI: 10.1016/j.livres.2022.12.002
MUTYH is a potential prognostic biomarker and correlates with immune infiltrates in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. The development of biomarkers for early detection and monitoring of HCC has not shown significant progress. Meanwhile, the second adenomatous polyposis-related gene, MUTYH, which encodes a DNA glycosylase, has been observed in its contribution to oxidative DNA damage repair. Abnormal expression of MUTYH can reduce cell survival rate. Therefore, this study investigated the usefulness of MUTYH in diagnosing and prognosis HCC.
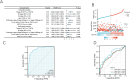
Materials and methods: Using The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data, we analyzed the prognostic value of MUTYH in HCC. We used logistic regression, Wilcoxon signed-rank test, and Kruskal-Wallis test to examine MUTYH expression concerning clinical-pathologic characteristics. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression methods and Kaplan-Meier analysis were applied to determine the related prognostic factors of HCC. The enrichment analysis (GSEA) was used to determine the critical pathways associated with MUTYH. The single-sample gene set enrichment analysis (ssGSEA) was conducted to examine the correlation between MUTYH expression and cancer immune infiltration.
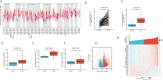
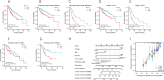
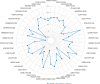
Results: The higher expression of MUTYH in HCC patients was associated with a poorer overall survival rate and a shorter disease-specific survival rate. The Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis showed that all differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between the high and low expression levels of MUTYH significantly enriched in the trace ligand-receptor interaction, cell cycle, oocyte meiosis, gap junction, and DNA replication. Group analysis revealed the signals of their open access. The neuron system, M phase, DNA repair, Rho GTPase effector, and cell cycle checkpoints were significantly enriched. ssGSEA showed a positive correlation between MUTYH expression and the infiltration levels of Th2 cells, NK cells, and T helper cells. Moreover, a negative correlation was found between MUTYH expression and the infiltration levels of dendritic cells (DCs) and cytotoxic cells.
Conclusions: MUTYH expression levels were positively correlated with immune checkpoint gene expression levels in HCC tissues. The expression level of MUTYH was related to the prognosis of HCC and the immune infiltration of HCC.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); Immune infiltrates; MUTYH; Prognostic biomarker.
© 2022 The Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of KeAi Communications Co. Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Over-expression of RRM2 predicts adverse prognosis correlated with immune infiltrates: A potential biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2023 Mar 28;13:1144269. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1144269. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37056349 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Biomarker DDOST and Its Correlation With Immune Infiltrates in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Genet. 2022 Jan 31;12:819520. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.819520. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35173766 Free PMC article.
-
TMEM147 Correlates with Immune Infiltration and Serve as a Potential Prognostic Biomarker in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2023 Jun 3;2023:4413049. doi: 10.1155/2023/4413049. eCollection 2023. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2023. PMID: 37305689 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of prognostic value and immunological roles of RAB22A in hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 3;14:1086342. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1086342. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36936971 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Rad51 as a prognostic biomarker correlated with immune infiltration in hepatocellular carcinoma.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):2664-2675. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1938470. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34115569 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
PRR13 expression as a prognostic biomarker in breast cancer: correlations with immune infiltration and clinical outcomes.Front Mol Biosci. 2025 Mar 3;12:1518031. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1518031. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40099041 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang G, Lu X, Du Q, et al. Diagnostic value of the γ-glutamyltransferase and alanine transaminase ratio, alpha-fetoprotein, and protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist II in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci Rep. 2020;10 doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70241-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
