Fluence and Dose Distribution Modeling of an Ultraviolet Light Disinfection Process for Pathogen Inactivation Efficiency Evaluation
- PMID: 39959059
- PMCID: PMC11822701
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c05715
Fluence and Dose Distribution Modeling of an Ultraviolet Light Disinfection Process for Pathogen Inactivation Efficiency Evaluation
Abstract
This study addresses the need to utilize bench-scale experimental results for ultraviolet (UV) light disinfection on solid food surfaces by proposing a novel framework to evaluate the fluence rate field of arbitrarily placed UV sources to ensure proper disinfection in industrial-scale food processing. Despite extensive research establishing UV fluence values for disinfection of various food types, industrial applications often face challenges due to nonhomogeneous UV distribution. This study introduces a method capable of determining the fluence distribution on solid food and food contact surfaces in both static and moving environments. Additionally, it aids in selecting the appropriate light sources and irradiation times. Our model leverages UV radiation models from different engineering disciplines to determine the UV fluence and dose distribution on the surface of convex objects. This helps to understand and optimize processes for proper decontamination, improved food quality, and a longer shelf life for processed products.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures





 , local surface normal
, local surface normal  and a line light source described with
the position vector of its center point
and a line light source described with
the position vector of its center point  and direction vector of its center line
and direction vector of its center line  inside the base coordinate system CSB.
inside the base coordinate system CSB.  gives the relative position of P from the lamp center point. In the lamp-focused approach,
equations are described in local (lamp) coordinate system CSL.
gives the relative position of P from the lamp center point. In the lamp-focused approach,
equations are described in local (lamp) coordinate system CSL.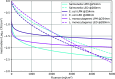
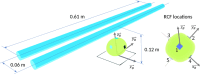



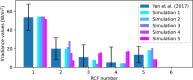


References
-
- Koutchma T.Reference Module in Food Science; Elsevier, 2016.
-
- Singh H.; Bhardwaj S. K.; Khatri M.; Kim K.-H.; Bhardwaj N. UVC radiation for food safety: An emerging technology for the microbial disinfection of food products. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 128084.10.1016/j.cej.2020.128084. - DOI
-
- Soro A. B.; Shokri S.; Nicolau-Lapeña I.; Ekhlas D.; Burgess C. M.; Whyte P.; Bolton D. J.; Bourke P.; Tiwari B. K. Current challenges in the application of the UV-LED technology for food decontamination. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 131, 264–276. 10.1016/j.tifs.2022.12.003. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
