Preparation and application evaluation of monoclonal antibodies against Monkeypox virus A29 protein
- PMID: 39959162
- PMCID: PMC11825512
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1547021
Preparation and application evaluation of monoclonal antibodies against Monkeypox virus A29 protein
Abstract
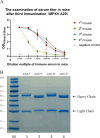
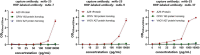
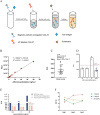
Monkeypox virus (MPXV) is a DNA virus belonging to the Orthopoxvirus genus of the Poxviridae family. It causes symptoms similar to Smallpox virus and is a zoonotic virus with widespread prevalence. Antigen detection is a fast and effective detection method. The MPXV A29 protein not only plays an important role in the virus lifecycle but also serves as a promising target for developing specific antibodies, which have significant potential for application in the diagnosis of MPXV. The coding sequences of the MPXV A29 protein, Cowpox virus (CPXV) 163 protein homolog and Vaccinia virus (VACV) A27 protein homolog were chemically synthesized, and all three recombinant proteins were expressed in Escherichia coli (BL21 Star). Then, the recombinant A29 protein was used as an antigen to immunize BALB/c mice, and a total of 4 monoclonal antibodies against A29 protein were obtained. Using two homologous proteins as reverse screening systems, a specific monoclonal antibody, mAb-25, against the A29 protein was screened. Then, the mAb-25 was used as a coating antibody to pair with other monoclonal antibodies, leading to the identification of a well-matched antibody pair. A chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay (CLEIA) and immunochromatographic gold assay were subsequently established using the optimal antibody pair. The experimental results indicate that monoclonal antibodies against the A29 protein hold significant potential for application in the diagnosis of MPXV.
Keywords: Monkeypox virus (MPXV); antigen detection; chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay; colloidal gold immunochromatography; monoclonal antibodies.
Copyright © 2025 Xiangjun, Xinlan, Ye, Chufan, Chen, Nami, Junxi, Yilan, Defu, Qinglin and Rushi.
Conflict of interest statement
XY, TC, QY, HD, WQ, and LR were employed by the Hunan Xuxiang Biotechnology Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Dashprakash M., Venkatesan G., Kumar A., Sankar M., Arya S., Ramakrishnan M. A., et al. (2019). Prokaryotic expression, purification and evaluation of goatpox virus ORF117 protein as a diagnostic antigen in indirect ELISA to detect goatpox. Arch. Virol. 164 1049–1058. 10.1007/s00705-019-04170-8 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

