Incentives in prescribing, dispensing and pharmaceutical spending: A scientometric mapping
- PMID: 39959435
- PMCID: PMC11826077
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.156306.2
Incentives in prescribing, dispensing and pharmaceutical spending: A scientometric mapping
Abstract
Introduction: Health systems worldwide are struggling to ensure the affordability of medicines. Prescription, dispensing, and pharmaceutical expenditures are key variables that highlight the need to understand how global scientific evidence is generated against factors (implicit and non-explicit) that influence these variables.
Objectives: Explore and provide a detailed description of the characteristics of the global scientific production of Open Access articles related to the prescription, dispensing and pharmaceutical expenditure faced by health systems worldwide.
Methods: A five-stage scientometric mapping was performed based on a systematic search of 8 databases. The five stages are: i) retrieval, ii) migration, iii) analysis, iv) visualization and v) interpretation.
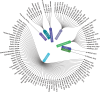
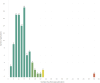
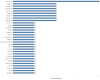
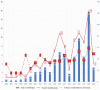
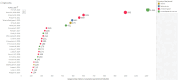
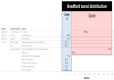
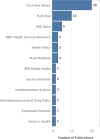
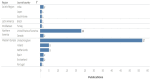
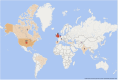
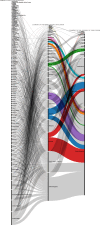
Results: A corpus of evidence from 103 systematic literature reviews was obtained, screened and sifted, visualizing the countries, authors, databases, journals, institutions and time periods that contributed most to evidence generation. Central research themes are identified and phenomena related to article publication are discussed.
Conclusions: The analysis reveals a clear leadership of the United Kingdom and the United States in scientific production on prescribing, dispensing and pharmaceutical expenditure in health systems worldwide. This scientific production is mainly focused on financing policies, pharmaceutical incentives and interventions, and rational use of medicines. There is also evidence of the scarcity of scientific production in Latin American publications and authors, which could generate interest for future research.
Keywords: Drug financing; Health systems; Price regulation; drug cost; insurance.
Copyright: © 2025 L. H TA et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures










References
-
- World Health Organization: WHO: En el Foro de la OMS sobre medicamentos, los países y la sociedad civil presionan para lograr una mayor transparencia y precios más justos. World Health Organization;2019. Reference Source
-
- Michán L, Muñoz-Velasco I: Cienciometría para ciencias médicas: definiciones, aplicaciones y perspectivas. InvestigacióN En EducacióN MéDica/InvestigacióN En EducacióN MéDica (En LíNea). 2013;2(6):100–106. 10.1016/s2007-5057(13)72694-2 - DOI
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

