Identification of CβS and ODC antimony resistance markers in anthroponotic cutaneous leishmaniasis field isolates by gene expression profiling
- PMID: 39959455
- PMCID: PMC11830360
- DOI: 10.1016/j.parepi.2025.e00413
Identification of CβS and ODC antimony resistance markers in anthroponotic cutaneous leishmaniasis field isolates by gene expression profiling
Abstract
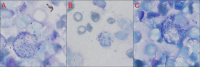
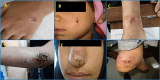
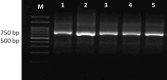
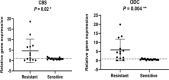
Antiparasitic resistance represents a serious global public health concern with tremendous economic and safety implications. This study intended to investigate the expression of the two major resistant markers: cystathionine β synthase (CβS) and ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) in antimony unresponsive Leishmania tropica isolates compared to responsive ones. Twenty-six patients were randomly selected from widely known foci of anthroponotic cutaneous leishmaniasis in southeastern Iran. Written informed consent of the patients was obtained. Two smears were prepared from the edge of each active lesion; one for microscopic direct smear preparation and the other for inoculation into monophasic NNN media, then for mass production of promastigotes into RPMI-1640 monophasic culture for performing nested PCR and gene expression quantification by real-time PCR. Twenty-six patients consisting of 13 unresponsive and 13 responsive equally distributed among female and male groups. All cases were identified to be L. tropica. Both resistant gene markers were significantly up-regulated in unresponsive and responsive isolates. The findings showed that CβS and ODC are directly linked with the resistance to L. tropica. Alternative drugs or combination therapy and monitoring drug resistance to prevent the spread of resistant isolates are proper strategies to control the disease.
Keywords: Antimonial resistance; Cystathionine β synthase; Genetic markers; Leishmania tropica; Ornithine decarboxylase.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Unresponsiveness to meglumine antimoniate in anthroponotic cutaneous leishmaniasis field isolates: analysis of resistance biomarkers by gene expression profiling.Trop Med Int Health. 2018 Jun;23(6):622-633. doi: 10.1111/tmi.13062. Epub 2018 May 21. Trop Med Int Health. 2018. PMID: 29709098
-
Involvement of tryparedoxin peroxidase (TryP) and trypanothione reductase (TryR) in antimony unresponsive of Leishmania tropica clinical isolates of Iran.Acta Trop. 2022 Jun;230:106392. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2022.106392. Epub 2022 Mar 8. Acta Trop. 2022. PMID: 35276060
-
Gene expression analysis of antimony resistance in Leishmania tropica using quantitative real-time PCR focused on genes involved in trypanothione metabolism and drug transport.Arch Dermatol Res. 2019 Jan;311(1):9-17. doi: 10.1007/s00403-018-1872-2. Epub 2018 Nov 2. Arch Dermatol Res. 2019. PMID: 30390113
-
Expression analysis of activated protein kinase C gene (LACK1) in antimony sensitive and resistant Leishmania tropica clinical isolates using real-time RT-PCR.Int J Dermatol. 2016 Sep;55(9):1020-6. doi: 10.1111/ijd.13321. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Int J Dermatol. 2016. PMID: 27336481
-
Changes in the Epidemiology of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Northeastern Iran.Turkiye Parazitol Derg. 2020 Mar 20;44(1):52-57. doi: 10.4274/tpd.galenos.2019.6137. Turkiye Parazitol Derg. 2020. PMID: 32212595 Review.
References
-
- "World Health Organization . WHO; Geneva: 2023. Global report on neglected tropical diseases.
-
- Aflatoonian M.R., Sharifi I., Aflatoonian B., Shirzadi M.R., Gouya M.M., Kermanizadeh A. A review of impact of bam earthquake on cutaneous leishmaniasis and status: epidemic of old foci, emergence of new foci and changes in features of the disease. J. Arthropod. Borne Dis. 2016;10(3):271. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

