Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Choroid Visualization for Myopia: A Comprehensive Scoping Review
- PMID: 39959595
- PMCID: PMC11823532
- DOI: 10.4103/meajo.meajo_154_24
Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Choroid Visualization for Myopia: A Comprehensive Scoping Review
Abstract
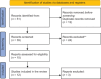
Numerous artificial intelligence (AI) models, including deep learning techniques, are being developed to segment choroids in optical coherence tomography (OCT) images. However, there is a need for consensus on which specific models to use, requiring further synthesis of their efficacy and role in choroid visualization in myopic patients. A systematic literature search was conducted on three main databases (PubMed, Web of Science, and Scopus) using the search terms: "Machine learning" OR "Artificial Intelligence" OR "Deep learning" AND "Myopia" AND "Choroid" OR "Choroidal" from inception to February 2024 removing duplicates. A total of 12 studies were included. The populations included myopic patients with varying degrees of myopia. The AI models applied were primarily deep learning models, including U-Net with a bidirectional Convolutional Long Short-Term Memory module, LASSO regression, Attention-based Dense U-Net network, ResNeSt101 architecture training five models, and Mask Region-Based Convolutional Neural Network. The reviewed AI models demonstrated high diagnostic accuracy, including sensitivity, specificity, and area under the curve values, in identifying and assessing myopia-related changes. Various biomarkers were assessed, such as choroidal thickness, choroidal vascularity index, choroidal vessel volume, luminal volume, and stromal volume, providing valuable insights into the structural and vascular changes associated with the condition. The integration of AI models in ophthalmological imaging represents a significant advancement in the diagnosis and management of myopia. The high diagnostic accuracy and efficiency of these models underscore their potential to revolutionize myopia care, improving patient outcomes through early detection and precise monitoring of disease progression. Future studies should focus on standardizing AI methodologies and expanding their application to broader clinical settings to fully realize their potential in ophthalmology.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; choroid; deep learning; myopia.
Copyright: © 2024 Middle East African Journal of Ophthalmology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Application of Artificial Intelligence and Deep Learning for Choroid Segmentation in Myopia.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2022 Feb 1;11(2):38. doi: 10.1167/tvst.11.2.38. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 35212716 Free PMC article.
-
Automatic Screening and Identifying Myopic Maculopathy on Optical Coherence Tomography Images Using Deep Learning.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2021 Nov 1;10(13):10. doi: 10.1167/tvst.10.13.10. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2021. PMID: 34751744 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of a deep convolutional neural network in the detection of myopic macular diseases using swept-source optical coherence tomography.PLoS One. 2020 Apr 16;15(4):e0227240. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227240. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32298265 Free PMC article.
-
Role of artificial intelligence, machine learning and deep learning models in corneal disorders - A narrative review.J Fr Ophtalmol. 2024 Sep;47(7):104242. doi: 10.1016/j.jfo.2024.104242. Epub 2024 Jul 15. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2024. PMID: 39013268 Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence Applications to Measure Food and Nutrient Intakes: Scoping Review.J Med Internet Res. 2024 Nov 28;26:e54557. doi: 10.2196/54557. J Med Internet Res. 2024. PMID: 39608003 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Holden BA, Fricke TR, Wilson DA, Jong M, Naidoo KS, Sankaridurg P, et al. Global prevalence of myopia and high myopia and temporal trends from 2000 through 2050. Ophthalmology. 2016;123:1036–42. - PubMed
-
- Morgan IG, French AN, Ashby RS, Guo X, Ding X, He M, et al. The epidemics of myopia: Aetiology and prevention. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2018;62:134–49. - PubMed
-
- Wong TY, Ferreira A, Hughes R, Carter G, Mitchell P. Epidemiology and disease burden of pathologic myopia and myopic choroidal neovascularization: An evidence-based systematic review. Am J Ophthalmol. 2014;157:9–25.e12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources