Association between triglyceride-glucose index and its composite obesity indexes and cardio-renal disease: analysis of the NHANES 2013-2018 cycle
- PMID: 39959622
- PMCID: PMC11825323
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1505808
Association between triglyceride-glucose index and its composite obesity indexes and cardio-renal disease: analysis of the NHANES 2013-2018 cycle
Abstract
Background: The association between triglyceride-glucose (TYG) and its composite obesity indexes and cardio-renal disease in the American population remains insufficiently researched.
Methods: This study examined a cohort of 11,491 American adults aged 20 years and older from the 2003-2018 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). To explore the associations between TYG, TyG-Waist-to-Height Ratio (TyG-WHtR), TyG-Body Mass Index (TyG-BMI), TyG-Waist Circumference (TyG-WC), and chronic kidney disease (CKD), cardiovascular disease (CVD), and cardiorenal syndrome (CRS), we utilized weighted multivariate logistic regression, restricted cubic spline (RCS), Receiver operating characteristic (ROC), and subgroup analyses.
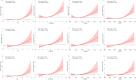
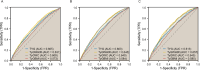
Results: Adjusted for confounding factors, there are positive associations between the likelihood of CKD, CVD, and CRS, as well as TYG and its composite obesity indexes. The TYG index was correlated most strongly with CKD (OR 1.42, 95% CI 1.11, 1.82; P = 0.007), while TyG-WHtR had the strongest correlations with CVD (OR 1.63, 95% CI 1.19, 2.22; P = 0.003) and CRS (OR 1.44, 95% CI 1.00, 2.08; P = 0.055). A nonlinear connection was found by RCS analysis between TYG and its composite obesity indexes with CKD (P for overall < 0.001, P for nonlinear < 0.05), while the association with CVD and CRS was predominantly linear (P for overall < 0.001, P for nonlinear > 0.05). Based on ROC curves, TyG-WHtR and TyG-WC emerged as more reliable diagnostic tools than TYG for cardiac and renal diseases. According to subgroup analyses, TyG and its composite obesity measurements were more strongly associated with CKD in younger individuals (≤ 50), males, and those with diabetes mellitus (P for interaction 0.05).
Conclusions: The TyG-WHtR and TyG-WC are associated with an increased risk of cardiac and renal disease, indicating enhanced diagnostic accuracy. These metrics provide an effective tool for identifying early cardiorenal disease and improving risk stratification.
Keywords: NHANES; TyG related indicators; cardiorenal syndrome; cardiovascular disease; chronic kidney disease.
Copyright © 2025 Wu, Liu and Cao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- GBD 2021 Causes of Death Collaborators . Global burden of 288 causes of death and life expectancy decomposition in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet (London England). (2024) 403:2100–32. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00367-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

