Impact of strict IGF1 control on quality-of-life scores in patients with acromegaly
- PMID: 39959623
- PMCID: PMC11825318
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1516899
Impact of strict IGF1 control on quality-of-life scores in patients with acromegaly
Abstract
Objective: Examine, in a real-world setting, whether strict normalization of modestly elevated insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1) results in clinical and health-related quality of life benefits in patients with acromegaly using an open-label, non-randomized, 6-month prospective interventional study.
Methods: In patients with acromegaly and modest IGF1 elevation, strict IGF1 control was achieved by addition or dose escalation of pegvisomant. Clinical and biochemical parameters were assessed at baseline, 1 and 3 months for pegvisomant dose titration, and at 6 months. The Patient-Assessed Acromegaly Symptom Questionnaire (PASQ), the Acromegaly Quality of Life questionnaire (AcroQoL) and the Acromegaly Disease Activity Tool (ACRODAT®) were completed at baseline and at 6 months.
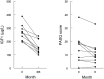
Results: Ten patients (8 males) with mean age of 50.7 years participated in the study. All patients had a macroadenoma and nine had prior transsphenoidal surgeries. At time of screening, six patients were on a somatostatin analog, two on pegvisomant, and two on pegvisomant and a somatostatin analog. After six months of dose escalation or the addition of pegvisomant, IGF1 decreased from 1.22 ± 0.14 to 0.87 ± 0.20 times the upper limit of normal (p=0.001). PASQ score decreased by 3.5 (p=0.02) and the ACRODAT® overall status decreased by 50.5 (p=0.001); however, there was no difference in the AcroQoL score. Hemoglobin A1c and liver enzymes did not differ and repeat MRI of the sella at 6 months showed no change.
Conclusions: In this pilot study, stricter control of modest IGF1 elevations led to symptomatic improvement as measured by the PASQ score. These findings prompt larger prospective trials.
Keywords: acromegaly; clinical trial; insulin-like growth factor 1; pegvisomant; quality-of-life.
Copyright © 2025 Gandhi, Denis, Holmes, Rivera, van Uum, Ezzat and Chik.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

