Identification of Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers of Carotid Atherosclerosis in Obese Populations
- PMID: 39959637
- PMCID: PMC11829119
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S504480
Identification of Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers of Carotid Atherosclerosis in Obese Populations
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the potential mechanisms and biomarkers between Obesity (OB) and carotid atherosclerosis (CAS).
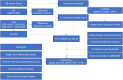
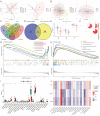
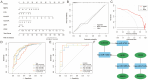
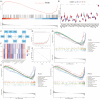
Methods: The GSE12828, GSE125771, GSE43292, and GSE100927 datasets were combined and normalized to obtain CAS-related differentially expressed genes (DEGs), and OB-related DEGs were obtained from the GSE151839 dataset and the GeneCards database. Unsupervised cluster analysis was conducted on CAS samples based on the DEGs of CAS and OB. Subsequently, immune infiltration analysis and gene set enrichment analysis (GESA) were performed. 61 machine learning models were developed to screen for Hub genes. The Single-gene GESA focused on calcium signaling pathway-related genes (CaRGs). Finally, high-fat diet-fed C57BL/6J ApoE-/- mice were used for in vivo validation.
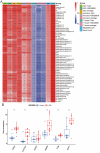
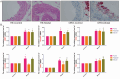
Results: MMP9, PLA2G7, and SPP1 as regulators of the immune infiltration microenvironment in OB patients with CAS, and stratified CAS samples into subtypes with differences in metabolic pathways based on OB classification. Enrichment analysis indicated abnormalities in immune and inflammatory responses, the calcium signaling, and lipid response in obese CAS patients. The RF+GBM model identified CD52, CLEC5A, MMP9, and SPP1 as Hub genes. 15 CaRGs were up-regulated, and 12 were down-regulated in CAS and OB. PLCB2, PRKCB, and PLCG2 were identified as key genes in the calcium signaling pathway associated with immune cell infiltration. In vivo experiments showed that MMP9, PLA2G7, CD52, SPP1, FYB, and PLCB2 mRNA levels were up-regulated in adipose, aortic tissues and serum of OB and AS model mice, CLEC5A was up-regulated in aorta and serum, and PRKCB was up-regulated in adipose and serum.
Conclusion: MMP9, PLA2G7, CD52, CLEC5A, SPP1, and FYB may serve as potential diagnostic biomarkers for CAS in obese populations. PLCB2 and PRKCB are key genes in the calcium signaling pathway in OB and CAS. These findings offer new insights into clinical management and therapeutic strategies for CAS in obese individuals.
Keywords: bioinformatics; calcium signaling pathway; carotid atherosclerosis; machine learning model; obesity; unsupervised clustering analysis.
© 2025 Wu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



References
-
- The National Health Commission’s bureau of disease prevention and control. Report on the Nutrition and Chronic Disease Status of Chinese Residents. Acta Nutrimenta Sinica. 2020;42(6):521.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

