Cancer diagnosis and prognosis after initiation of hemodialysis: multicenter Japan CANcer and DialYsis (J-CANDY) study
- PMID: 39959911
- PMCID: PMC11826057
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sfae430
Cancer diagnosis and prognosis after initiation of hemodialysis: multicenter Japan CANcer and DialYsis (J-CANDY) study
Abstract
Background: Cancer is a leading cause of death among patients on hemodialysis; however, the data on its diagnosis, treatment and prognosis are limited. Here we analyzed the surgical practice patterns and outcomes of patients on hemodialysis with cancer and compared them with those of general cancer patients from the National Cancer Center database.
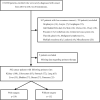
Methods: This nationwide registry enrolled hemodialysis patients who were subsequently diagnosed with primary cancers of the kidney, colorectum, stomach, lung, liver, bladder, pancreas and breast in 20 hospitals in Japan between 2010 and 2012. The primary endpoint was the overall 3-year survival rate. We also examined the association of factors with mortality using Cox regression analysis.
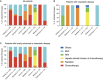
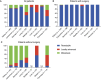
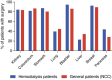
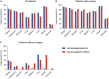
Results: Of the 502 patients, 370 (74%) underwent surgery. More than half of the patients (57%) were asymptomatic at diagnosis and diagnosed with cancer through screening. Among the patients who underwent surgery, most (99%) had resectable cancers; while among those who did not undergo surgery, more than half (52%) had metastatic cancers. The 3-year overall survival in the surgery and non-surgery groups was 83% and 32%, respectively. Non-cancer-related deaths were dominant (80%) in the surgery group, whereas cancer-related deaths were dominant in the non-surgery group (70%). Pancreatic cancer and anemia were associated with a poor prognosis in the surgery group. Surgery and 3-year overall survival rates were comparable between the patients on hemodialysis and the general cancer patients.
Conclusion: Prognosis in hemodialysis cancer patients might be equivalent to that of general cancer patients.
Keywords: cancer; hemodialysis; prognosis; surgery.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the ERA.
Conflict of interest statement
M.Y. receives research grants from Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma and Boehringer Ingelheim. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Masakane I, Taniguchi M, Nakai S et al. Annual Dialysis Data Report 2015, JSDT Renal Data Registry. Ren Replace Ther 2018;4:19. 10.1186/s41100-018-0149-8 - DOI

